Ce sujet a été résolu
ChevalierLion
1 an
Post ou cancer.
Vidéo d'utilité publique :
https://youtu.be/ASd7PmlHcwc
il y a 8 mois
Anthony_A3
8 mois
Post.

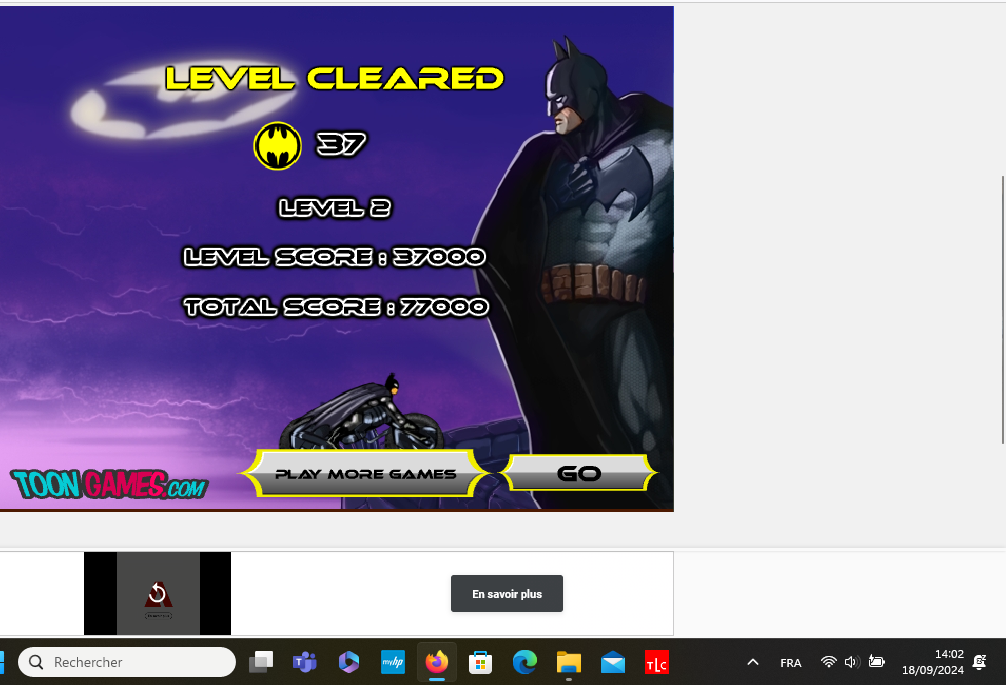

This Case Is Beyond BRUTAL In May of 2012, Hannah Windsor went missing. The police began searching for her...however, after a chilling confession from her boyfriend, they uncovered one of the UK's most chilling crimes.
The DISTURBING Case of Janine Balding
 https://en.wikipedia.org/[...]/Murder_of_Janine_Balding
https://en.wikipedia.org/[...]/Murder_of_Janine_Balding















Merci pour le up

En plein camp d’entraînement à Chiang Maï

il y a 8 mois
Merci pour le up

De rien; Je vais encore plus up si tu y tiens.

Edit : et nique Dupont Moretti.

7 Worst Disasters That Were EASY to Prevent
Schoharie Lousiane disaster could easily have been avoided. 20 people died. It was on October 6th 2018 when Amy Stenberg's friends and family plan to celebrate her 30th bithday at a brewery about 1 hour away. After initial limo rental was cancelled in last minute they hired on from prestige limousine of Wilton. Their order was a 2001 Ford Excursion XLT. The SUV weigted 10 0000 pounds. It was split in half and extending its lenght by adding additionnal 12 feet to morph into a bus like structure. The group of 17 boarded the vehicule at 1 : 30 pm. Among them, 4 sisters, 2 btothers, 3 army veterans and 2 newlywed couples. Flashing neon lights were inside the limousine. Plus worn out padded benches and floorboards marred by rust. One of the partyer texts to a friend that didn't join the party that the limo sounded like it was going to explode. The route was from Amsterdam to Cooperstown. Eventually the car drove down a steep hill towards a tea junction in Skari, the driver hit the brakes urgently but the brake system faded. The limousine speed rapidly increased, surpassing 160 kilometers per hour. Desperate to avoid a collision with a car bypassed the stop sign and kening into the driveway of a nearby restaurant. On the opposite side of the road, the parking lot of a country store. The limousine collided with a parked Toyota highlander hurdling the SUV 80 feet through the air.. 2 unsuspecting pedestrians a father and son in law were caught in the path of destruction when the highlander struck them. But the SUV continued in a speed of 130 kilometers per hour. towards its final resting place. The exterior of the passenger compartment was relatively intact masking the gruesome reality. The collision instantly claimed the lives of 16 individuals. The absence of seat belts exacerbated the situation as the passengers bodies collided within the cabin. Emergency responders dispatched. In the aftermath, the death roll went up to 20. All 18 individuals in the limousine died.
After investigation, some troubling informations came to light. The limousine was in poor conditions with numerous mechanical issues not adressed. The company that stretched the limousine in 2001 didn't have the required license and failed to upgrade the brakes to handle the extra weight. Even though the state department of transportation classified the excursion as a bus, it hadn't gone through the necessary certification or inspection process. The department issues 2 several orders for the limo to be taken off the road in the months before the accident. Despite this, the sticker indicating the vehicle's unfitness was missing at the time. Additionally the company already had been ordered to surrender the registration and licence plates for all his vehicles including the limousine because of previous violations. The company received 22 citations for violations within 24 months before the crash. On September, 3 of their vehicles failed inspections and were cited for infractions such as defective emergencyexits and malfunctioning brakes. The driver was not peroperly licensed to drive the vehicle either and was not subjected to mandatory drug testing. as an autopsie would later reveal the presence of THC in his system. Numerous last seat belts in the limousine went unnoticed by the passengers because they were hiding beneath benches. Numerous questions were raised about the company's clandestine tie to lax enforcements; Shahed Hussin, the company's owner had a controversial part, having been an informant for the FBI in a terrorism investigation. However he returned in Pakistan 6 months before the crash but his connections couldn't shield him from intending illegal actions. In March 2019 a jury indicted him and his son Nauman Hussein on charges of manslaughter and criminally negligent homicide. The youg Hussein allowed the limousine to remain on service despite knowing it was unsafe.
.
Biescas campsite disaster was another accident easily avoidable. It was in mountains of northern Spain. Inside their camper, Jose Sole, his wife and his daughter watch a torrent of water flow unstoppably below their window. A wave flood carrying logs and rocks had stormed through the sudden onslaugh threw them into a desperate struggle for survival. The shadow of death looming. Dozen of others weren't as lucky. On August 7th 1996, Spanish National Institute of Meteorology warned about incoming storm for the northern part of che country. Heavy summer rains are frequent in this region. But this one was more intensive with the province of Aragon expected to be the most effected and nestled in the north of it deep in the purines mountain range lies the Sierra deas nevas campsite, one of the most beautiful in Inland Spain at the time who opened 6 years earlier and was known for its quality. In August over 600 guests registered at the site even through many decide to go on excursions, the place was swarming with people unfazed by the rain. People withdrew into camps and tents waiting for the rain to stop. However, half an hour later it was getting heavier. Still no one seemed aware that they were resting in a death trap. The campsite was built on a sediment deposit at the foothold of 2 steep hills but more importantly at the exit of the Arys ravine running between them. Since years it had been proned to water rushing through its channel during periods of heavy rain fall. The day of the disaster the rain was 200 to 250 mm. One quarter of that rainfall came down in just 8 minutes. The ground couldn't absorb so many so the excess flowed down the ravine, bringing logs and rocks, causing blockage at the bridge which broke under pressure, sending a wave of water and debris into the campsite. As the waves swept through, guests had to survive.
Many were caught by surprise and had no time to escape Some struggled to stay afloat as the water carried them down the stream along with tents, furniture, cars and even large campers. Sergio Murillo, one of the survivors, remembers how the current dragged him and his family. He got trapped in the branches of a falling tree, climbed it and foud rescue in the high canopy. But his parents and 2 brothers were taken away by the torrent. Other campers were out of reach of the water but still trapped inside their vans and trailers floating like boats on the water. The flood eventually declined and lost its destructive power. Brown muddy water still poured because of the rain and prevented people from escaping or eaching those still in danger. News of the disaster reached the village of Biescas and its residents along with a small firefighting team rused to assist. By the night, hundreds of soldiers, red cross members and volunteers were at the night. Injured people were sent to Biescas to receive first aid before being sent to hospital. Only by the next morning they knew the scale of the tragedy. Demolished cars and trailers were everywhere. Even through train dogs were brought in, the mud hardened quickly so rescuers locate the bodies of both survivors and the dead head buried beneath. The only way to scan the groud was with the help of sticks which was slow and wearing process. The torrent had carried bodies into the Gallego river with one victim found 13 kilometers away in the Sabado swarm. The operation's duration was several days. Police didn't have informations on guests nor did they know their identities. The reception computer was destroyed in the flood asn rendered useless. Temporary shelter was established. Experts claimed a flood like this happens once every 200 years.
Some blamed the camp's location at the mouth of the ravine that had high flood potential. 70 years before, after another flood, authorities built a channel through the midline of the sediment deposit to direct water in case of heavy rainfall and protect the area. Futhermore, 36 retention dams were built along the Aris ravine to prevent landslides. However the system to prevent flood only contributed to the 1996 tragedy. During the storm, the excess water rushed down the ravine. This overwhelmed and broke most of the dams releasing the sediments that they stored. As this happened it picked up roughly 6 000 truckloads of logs, mud and rocks. Eventually the debris was stopped by a bridge above the campground bit it couldn't bear the pressure and broke. 87 people died in the campsite disaster with the last body only discovered 1 year later. It was fortunate that there were 500 survivors as most were absent from the park at the time. The mayor responded to accusations by saying the campsite was built according to regulations. Yet records showed that before the construction, a government issued a negative report because of the location's risk. The government recklessly negleted his opinion. The court rejected the criminal charge as the accident was seen as exceptionnal and unpredictable and a decade long battle happened between the families and the authorities. In 2005 the National Court recognized the authorities rseponsability and ordered the government and the ministry of environment to jointly indemnify 63 of the 87 fatalities with 11,2 million euros. The government never paid its share of compensation. The campsite was rebuilt but in a safer location. A memorial was erected where it once stood.
Edit : et nique Dupont Moretti.
Schoharie Lousiane disaster could easily have been avoided. 20 people died. It was on October 6th 2018 when Amy Stenberg's friends and family plan to celebrate her 30th bithday at a brewery about 1 hour away. After initial limo rental was cancelled in last minute they hired on from prestige limousine of Wilton. Their order was a 2001 Ford Excursion XLT. The SUV weigted 10 0000 pounds. It was split in half and extending its lenght by adding additionnal 12 feet to morph into a bus like structure. The group of 17 boarded the vehicule at 1 : 30 pm. Among them, 4 sisters, 2 btothers, 3 army veterans and 2 newlywed couples. Flashing neon lights were inside the limousine. Plus worn out padded benches and floorboards marred by rust. One of the partyer texts to a friend that didn't join the party that the limo sounded like it was going to explode. The route was from Amsterdam to Cooperstown. Eventually the car drove down a steep hill towards a tea junction in Skari, the driver hit the brakes urgently but the brake system faded. The limousine speed rapidly increased, surpassing 160 kilometers per hour. Desperate to avoid a collision with a car bypassed the stop sign and kening into the driveway of a nearby restaurant. On the opposite side of the road, the parking lot of a country store. The limousine collided with a parked Toyota highlander hurdling the SUV 80 feet through the air.. 2 unsuspecting pedestrians a father and son in law were caught in the path of destruction when the highlander struck them. But the SUV continued in a speed of 130 kilometers per hour. towards its final resting place. The exterior of the passenger compartment was relatively intact masking the gruesome reality. The collision instantly claimed the lives of 16 individuals. The absence of seat belts exacerbated the situation as the passengers bodies collided within the cabin. Emergency responders dispatched. In the aftermath, the death roll went up to 20. All 18 individuals in the limousine died.
After investigation, some troubling informations came to light. The limousine was in poor conditions with numerous mechanical issues not adressed. The company that stretched the limousine in 2001 didn't have the required license and failed to upgrade the brakes to handle the extra weight. Even though the state department of transportation classified the excursion as a bus, it hadn't gone through the necessary certification or inspection process. The department issues 2 several orders for the limo to be taken off the road in the months before the accident. Despite this, the sticker indicating the vehicle's unfitness was missing at the time. Additionally the company already had been ordered to surrender the registration and licence plates for all his vehicles including the limousine because of previous violations. The company received 22 citations for violations within 24 months before the crash. On September, 3 of their vehicles failed inspections and were cited for infractions such as defective emergencyexits and malfunctioning brakes. The driver was not peroperly licensed to drive the vehicle either and was not subjected to mandatory drug testing. as an autopsie would later reveal the presence of THC in his system. Numerous last seat belts in the limousine went unnoticed by the passengers because they were hiding beneath benches. Numerous questions were raised about the company's clandestine tie to lax enforcements; Shahed Hussin, the company's owner had a controversial part, having been an informant for the FBI in a terrorism investigation. However he returned in Pakistan 6 months before the crash but his connections couldn't shield him from intending illegal actions. In March 2019 a jury indicted him and his son Nauman Hussein on charges of manslaughter and criminally negligent homicide. The youg Hussein allowed the limousine to remain on service despite knowing it was unsafe.
.
Biescas campsite disaster was another accident easily avoidable. It was in mountains of northern Spain. Inside their camper, Jose Sole, his wife and his daughter watch a torrent of water flow unstoppably below their window. A wave flood carrying logs and rocks had stormed through the sudden onslaugh threw them into a desperate struggle for survival. The shadow of death looming. Dozen of others weren't as lucky. On August 7th 1996, Spanish National Institute of Meteorology warned about incoming storm for the northern part of che country. Heavy summer rains are frequent in this region. But this one was more intensive with the province of Aragon expected to be the most effected and nestled in the north of it deep in the purines mountain range lies the Sierra deas nevas campsite, one of the most beautiful in Inland Spain at the time who opened 6 years earlier and was known for its quality. In August over 600 guests registered at the site even through many decide to go on excursions, the place was swarming with people unfazed by the rain. People withdrew into camps and tents waiting for the rain to stop. However, half an hour later it was getting heavier. Still no one seemed aware that they were resting in a death trap. The campsite was built on a sediment deposit at the foothold of 2 steep hills but more importantly at the exit of the Arys ravine running between them. Since years it had been proned to water rushing through its channel during periods of heavy rain fall. The day of the disaster the rain was 200 to 250 mm. One quarter of that rainfall came down in just 8 minutes. The ground couldn't absorb so many so the excess flowed down the ravine, bringing logs and rocks, causing blockage at the bridge which broke under pressure, sending a wave of water and debris into the campsite. As the waves swept through, guests had to survive.
Many were caught by surprise and had no time to escape Some struggled to stay afloat as the water carried them down the stream along with tents, furniture, cars and even large campers. Sergio Murillo, one of the survivors, remembers how the current dragged him and his family. He got trapped in the branches of a falling tree, climbed it and foud rescue in the high canopy. But his parents and 2 brothers were taken away by the torrent. Other campers were out of reach of the water but still trapped inside their vans and trailers floating like boats on the water. The flood eventually declined and lost its destructive power. Brown muddy water still poured because of the rain and prevented people from escaping or eaching those still in danger. News of the disaster reached the village of Biescas and its residents along with a small firefighting team rused to assist. By the night, hundreds of soldiers, red cross members and volunteers were at the night. Injured people were sent to Biescas to receive first aid before being sent to hospital. Only by the next morning they knew the scale of the tragedy. Demolished cars and trailers were everywhere. Even through train dogs were brought in, the mud hardened quickly so rescuers locate the bodies of both survivors and the dead head buried beneath. The only way to scan the groud was with the help of sticks which was slow and wearing process. The torrent had carried bodies into the Gallego river with one victim found 13 kilometers away in the Sabado swarm. The operation's duration was several days. Police didn't have informations on guests nor did they know their identities. The reception computer was destroyed in the flood asn rendered useless. Temporary shelter was established. Experts claimed a flood like this happens once every 200 years.
Some blamed the camp's location at the mouth of the ravine that had high flood potential. 70 years before, after another flood, authorities built a channel through the midline of the sediment deposit to direct water in case of heavy rainfall and protect the area. Futhermore, 36 retention dams were built along the Aris ravine to prevent landslides. However the system to prevent flood only contributed to the 1996 tragedy. During the storm, the excess water rushed down the ravine. This overwhelmed and broke most of the dams releasing the sediments that they stored. As this happened it picked up roughly 6 000 truckloads of logs, mud and rocks. Eventually the debris was stopped by a bridge above the campground bit it couldn't bear the pressure and broke. 87 people died in the campsite disaster with the last body only discovered 1 year later. It was fortunate that there were 500 survivors as most were absent from the park at the time. The mayor responded to accusations by saying the campsite was built according to regulations. Yet records showed that before the construction, a government issued a negative report because of the location's risk. The government recklessly negleted his opinion. The court rejected the criminal charge as the accident was seen as exceptionnal and unpredictable and a decade long battle happened between the families and the authorities. In 2005 the National Court recognized the authorities rseponsability and ordered the government and the ministry of environment to jointly indemnify 63 of the 87 fatalities with 11,2 million euros. The government never paid its share of compensation. The campsite was rebuilt but in a safer location. A memorial was erected where it once stood.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

The Ship Sinking MS Estonia (Disaster Documentary)
The Baltic Sea, enclosed by Central and Northern European countries, is one of the most extraordinary and beautiful seas. However, its beauty tends to be treacherous as the harsh climate in the Baltic often makes it pretty inhospitable. For centuries the Baltic Sea has been infamous among seafarers, with a number of shipwrecks lying on the bottom of the sea to prove it. In 1994, the stormy waters of the Baltic took away the lives of hundreds of victims in one of the greatest peacetime sinkings in the history of Europe. The sinking happened on September 28th, 1994. It was not a small ship. it was supposed to be able to whistand bad weather. built in 1980 in Pampenbourg West Germany, the ship was a 11 deck vessel and 515,16 feet in lenght with a tonnage of 15,598 gross tons. It was designed to accommodate 2 000 passengers and 460 cars. The ship sealed under the flags of 4 different operators for 14 years and then on Janury 1993, It was purchased by Estlineto become the largest country's vessel. For more than 1 year and half, it sealed from Tallin to Stockholm. On September 28th 1994, it was boarded by 803 passengers plus 186 crew members. That makes it 989 people in total. When it left, weather was nice but once it sealed away it began to change. Wind speed was between 15 and 20 mps. It's moderate gale but also calls for a warning gale pennant. Strong winds blowing from the port was causing problems as the ship began to slightly starboard. But it was not just because of the wind starting to lean on one side. Before leaving port, it was fully load with vehicles and cargo but in such a way the weight of the cargo wasn't arranged evenly. This made the ship leaning and the strong wind made it worse. Aroud 1 : 00 am, a giant wave hit the boat and this was followed by the sound of a metallic bang from the bow. Sailors on teh storage deck reported it to the second officer on the watch who ordered the inspection of the loading ramp and visor.
In the bow the boat had a feature called the visor. The visor allows the bow to articulat eup and down, allowing access to the loading ramp and cargo deck. The inspection of the indicator lamps in the storage deck showed nothing wrong neither the visor nor the loading ramp. So the second officer kept the course at the same speed. However after the metallic bang, passengers and crew reported more unusual sounds in the following 10 minutes. At 1 : 15 am, the second officer for an inspection. This time there was no oneed to check the indicator lamps as instead of the visor, there was a massive opening on the bow. The visor detached from hinge, letting the ramp fall open. Practically withotu the bow, the water was rapidly entering the storage deck of the ship. The ship started to list heavily to starboard. All alarms were raised and all the engines were shut down to reduce the ship's speed. However the listing was unstoppable. In just 15 minutes, the ship had rolled 60 degrees and water was breaching into upper decks. A lot of passengers didn't even leave the cabin before the water could reach them. Those alerted by the water tried to run and to reach the upper decks but the water was coming so quickly that it closed all accesses to upper decks. The entire ship lost electricity. People were trapped in the dark.THose reaching the upper decks began pushing rafts and jumping into cold water of the Baltic sea who had the temperature of 10 degrees. Plus the rain and the turbulent sea made it more difficult. A lot of rafts were capsized or swallowed by waves. It takes a lot of strenght to overcome these massive waves in the cold and merciless Baltic sea. At 1 : 21 am, MS Estonia sent the first mayday signal. It was recorded by the marine rescue coordinating center at the finnish city of Turku but was very weak and unclear. 2 minutes later MS Estonia sent a direct message to MS Silja Europa, another ferry.
The third officer on the radio on MS Estonia reported a bad list and a blackout. Then he asked to MS Silja Europa and other fairies to come to their assistance. Due to the blackout he wasn't able to report the exact position of his ship. Still the captain of MS Silja Europa directed towards MS Estonia's route. He forwarded the call for help to MS Mariell and other ferries in the vicinity and rescue stations in Sweden and Finland. MS Estonia sent his coordinates 5 minutes after the first message. That was the last message heard from MS Estonia. At that moment the list was more than 90 degrees with the starboard side completly submerged. At 1 : 50 am, MS Estonia disappeared from radar screens. At 2 : 12 am, the MS Marielle was the first ferry to arrive at scene. They found life rafts scattered all over the place. Soon, 4 other ferries arrived, including the MS Silja Europa whose captian was assigned to coordinate the rescue operations. Ferries launched life rafts into the water and used rescue slides to save people from the cold sea. Then the first helicopters arrived playing a significant role at saving the survivors. Finnish helicopters transferred them to land stations while the Swedish opted for a quicker and riskier solution : using cords to attach the life rafts and transfer them to ferries on the side. At the end, the decision proved to be on the spot as a single swedish helicopter saved more than all fairies combined. Out of 989 people in total, 310 reached outer decks. Half of them succedeed in boarding life rafts. rescuers saved 138 people. The rest died from drowning or from hypothermia. Around 650 people didn't even manage to leave the ship and sank with it. The ship was foud 300 meters deep and his visor a quarter of a mile away. Accident investigation commission from Estonia, Finland and Sweden was formed and investigation lasted from 2 years and half a year.
The visor failure was the reason why MS Estonia sank. The metallic noise was connected to the failure of the visor's locking mechanism. Later sounds probably came from the failures of other locking mechanisms. Once they all failed, the visor simply detached, leaving a massive opening on the bow and allowing the water to coem into the cargo deck. Because of the size of the gap, the water flooded the deck in just a couple of minutes, inciting listing to starboard. The visor was recovered from the seabed abd subjected to thorough to determine if it had any design flaws. It was determined that undner the condition of low waves, the strenght of the visor along with its locking mechanism and hinges was completly adequate. But the strong waves hitting the underside of the visor put too much pressure on the locking devices, the deck hinges and the lifting cylinder mountings. Due to the repeating pounding actinos fo the waves, the system collapsed and the visor broke off. Other incidents like this happened for vessels built in the same German shipyard. A few years before the disaster, MS Diana II had the same problem but the ferry crew saved the ship by reducing the vessel's speed and returning it the port. When the final report was published in 1997, a serie of controversies erupted. First came from the German manufacturer who claimed that the visor failure was not the starting point of the sinking but claimed that the ship was hold on the starboard side after which the water entered the cargo deck that the visor detached after the water flooded. A footage in 2020 recorded a 13 feet hole in the ship's shull and the rupture was put in connection with earlier controversies regarding the transport of military equipments. Estonian commission formed to consider new findings. But the last report said the rupture was too small to sink the ship in less than 1 hour. Finally it was revealed that the ferry wasn't even designed to be used outside coastal waters.
The Baltic Sea, enclosed by Central and Northern European countries, is one of the most extraordinary and beautiful seas. However, its beauty tends to be treacherous as the harsh climate in the Baltic often makes it pretty inhospitable. For centuries the Baltic Sea has been infamous among seafarers, with a number of shipwrecks lying on the bottom of the sea to prove it. In 1994, the stormy waters of the Baltic took away the lives of hundreds of victims in one of the greatest peacetime sinkings in the history of Europe. The sinking happened on September 28th, 1994. It was not a small ship. it was supposed to be able to whistand bad weather. built in 1980 in Pampenbourg West Germany, the ship was a 11 deck vessel and 515,16 feet in lenght with a tonnage of 15,598 gross tons. It was designed to accommodate 2 000 passengers and 460 cars. The ship sealed under the flags of 4 different operators for 14 years and then on Janury 1993, It was purchased by Estlineto become the largest country's vessel. For more than 1 year and half, it sealed from Tallin to Stockholm. On September 28th 1994, it was boarded by 803 passengers plus 186 crew members. That makes it 989 people in total. When it left, weather was nice but once it sealed away it began to change. Wind speed was between 15 and 20 mps. It's moderate gale but also calls for a warning gale pennant. Strong winds blowing from the port was causing problems as the ship began to slightly starboard. But it was not just because of the wind starting to lean on one side. Before leaving port, it was fully load with vehicles and cargo but in such a way the weight of the cargo wasn't arranged evenly. This made the ship leaning and the strong wind made it worse. Aroud 1 : 00 am, a giant wave hit the boat and this was followed by the sound of a metallic bang from the bow. Sailors on teh storage deck reported it to the second officer on the watch who ordered the inspection of the loading ramp and visor.
In the bow the boat had a feature called the visor. The visor allows the bow to articulat eup and down, allowing access to the loading ramp and cargo deck. The inspection of the indicator lamps in the storage deck showed nothing wrong neither the visor nor the loading ramp. So the second officer kept the course at the same speed. However after the metallic bang, passengers and crew reported more unusual sounds in the following 10 minutes. At 1 : 15 am, the second officer for an inspection. This time there was no oneed to check the indicator lamps as instead of the visor, there was a massive opening on the bow. The visor detached from hinge, letting the ramp fall open. Practically withotu the bow, the water was rapidly entering the storage deck of the ship. The ship started to list heavily to starboard. All alarms were raised and all the engines were shut down to reduce the ship's speed. However the listing was unstoppable. In just 15 minutes, the ship had rolled 60 degrees and water was breaching into upper decks. A lot of passengers didn't even leave the cabin before the water could reach them. Those alerted by the water tried to run and to reach the upper decks but the water was coming so quickly that it closed all accesses to upper decks. The entire ship lost electricity. People were trapped in the dark.THose reaching the upper decks began pushing rafts and jumping into cold water of the Baltic sea who had the temperature of 10 degrees. Plus the rain and the turbulent sea made it more difficult. A lot of rafts were capsized or swallowed by waves. It takes a lot of strenght to overcome these massive waves in the cold and merciless Baltic sea. At 1 : 21 am, MS Estonia sent the first mayday signal. It was recorded by the marine rescue coordinating center at the finnish city of Turku but was very weak and unclear. 2 minutes later MS Estonia sent a direct message to MS Silja Europa, another ferry.
The third officer on the radio on MS Estonia reported a bad list and a blackout. Then he asked to MS Silja Europa and other fairies to come to their assistance. Due to the blackout he wasn't able to report the exact position of his ship. Still the captain of MS Silja Europa directed towards MS Estonia's route. He forwarded the call for help to MS Mariell and other ferries in the vicinity and rescue stations in Sweden and Finland. MS Estonia sent his coordinates 5 minutes after the first message. That was the last message heard from MS Estonia. At that moment the list was more than 90 degrees with the starboard side completly submerged. At 1 : 50 am, MS Estonia disappeared from radar screens. At 2 : 12 am, the MS Marielle was the first ferry to arrive at scene. They found life rafts scattered all over the place. Soon, 4 other ferries arrived, including the MS Silja Europa whose captian was assigned to coordinate the rescue operations. Ferries launched life rafts into the water and used rescue slides to save people from the cold sea. Then the first helicopters arrived playing a significant role at saving the survivors. Finnish helicopters transferred them to land stations while the Swedish opted for a quicker and riskier solution : using cords to attach the life rafts and transfer them to ferries on the side. At the end, the decision proved to be on the spot as a single swedish helicopter saved more than all fairies combined. Out of 989 people in total, 310 reached outer decks. Half of them succedeed in boarding life rafts. rescuers saved 138 people. The rest died from drowning or from hypothermia. Around 650 people didn't even manage to leave the ship and sank with it. The ship was foud 300 meters deep and his visor a quarter of a mile away. Accident investigation commission from Estonia, Finland and Sweden was formed and investigation lasted from 2 years and half a year.
The visor failure was the reason why MS Estonia sank. The metallic noise was connected to the failure of the visor's locking mechanism. Later sounds probably came from the failures of other locking mechanisms. Once they all failed, the visor simply detached, leaving a massive opening on the bow and allowing the water to coem into the cargo deck. Because of the size of the gap, the water flooded the deck in just a couple of minutes, inciting listing to starboard. The visor was recovered from the seabed abd subjected to thorough to determine if it had any design flaws. It was determined that undner the condition of low waves, the strenght of the visor along with its locking mechanism and hinges was completly adequate. But the strong waves hitting the underside of the visor put too much pressure on the locking devices, the deck hinges and the lifting cylinder mountings. Due to the repeating pounding actinos fo the waves, the system collapsed and the visor broke off. Other incidents like this happened for vessels built in the same German shipyard. A few years before the disaster, MS Diana II had the same problem but the ferry crew saved the ship by reducing the vessel's speed and returning it the port. When the final report was published in 1997, a serie of controversies erupted. First came from the German manufacturer who claimed that the visor failure was not the starting point of the sinking but claimed that the ship was hold on the starboard side after which the water entered the cargo deck that the visor detached after the water flooded. A footage in 2020 recorded a 13 feet hole in the ship's shull and the rupture was put in connection with earlier controversies regarding the transport of military equipments. Estonian commission formed to consider new findings. But the last report said the rupture was too small to sink the ship in less than 1 hour. Finally it was revealed that the ferry wasn't even designed to be used outside coastal waters.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

500 People Trapped in a Submerged Subway
The in-depth story of the Zhengzhou Metro Line 5 Flooding Disaster 2021. A subway ride home quickly turns into a nightmare when over five hundred passengers get trapped in a flooded tunnel between two stations.
But how could such a life-threatening situation possibly unfold on a routine subway commute? Why was there no emergency response? And was this a natural disaster or a man-made catastrophe after all? Late July 2021 in China in Zhengzhou, Henan there was a storm and flooding that pushed the city's infrastructure beyond it's breaking point. It peaked on 20th July. In afternoon, rainfaill rates spiked over 8 inches per hour. Streets transformed into gushing river with water being 3 feets deep in some areas. Residents were trapped in work places or vehicles. Only to return home was by subway. However concerns grew whether subway system could handle such flooding from above the ground. The subway system was engineered to whistand flood by by sealing off impacted stations while keeping other sections oeprationnal. But as the day progressed, wate rbegan breaching overpowering pumping capabilities at multiple stations and causing power outages. The unrivaled downpour overpowered the whole system. In 4 pm when rainfall reached its maximum, subway authorities decided to close the stations most threatened by the flood, keeping the rest of the subway operationnal. Among the lines still functionning there was the line 5, the busiest of the entire system and accounting for 30% of the traffic of the entire system. City officials didn't want to prevent ten of thousands to reach their home. On 4 : 50 pm, scores of commuters boarded train number 0501 line at the Jingkai Center Square station. relieved to have caught the ride and no one knew they would embark on a disastrous trip. On 5 : 21 pm, emergency brake system suddently stopped the train. The system was triggered for unknown reason.
After a couple of minutes, the driver restarted it and continued down the track. At 5 : 40 pm, the train reached Haitansi station stopping several minutes, allowing passengers to disembark and others to board. After it, it resumed its journay to the next station, the Shakoulu station. 2 minutes later, the train stopped because of the emergency brake system. However it was for a good reason and water started going down the tracks. Unable to reach the next station, the driver attempted to reverse course and returned the train to the safety of Haitansi station. But after making 300 meters, the train was again stopped by the emergency brake system. Now it was stuck unable to go forward or back. What was strange was the amout of water coming from the Shakoulu station. Even if there was a bleach allowing water inside, standard protocols should ahve triggeredits immediate closure, sealing it to prevent the inflow. But in fact the water was coming from another source. 5 kilometers away from Shakoulou station, water had been pilling up around the Wulongkou parking lot for train operating on line 5. Because it was built on a lower Ling arena, the train lot was encircled by retaining wall to protect it from flooding. However the quality of the wall was inadequate to withstand the amount of rainfall. As the pressure increased, the wall gave away and let a torrent of water pour into the lot. From there it flowed through the subway tunnel downhill past Shakoulu and toward the track section where train number 0501 was trapped. Inside the train, 500 commuters. Water started to breach into the sixth carriage and quickly reached the ankles of passengers trapped in the upward slope leading to the Shaloulu station.
At 6 : 30 pm, aware of the unfolding situation, the train driver rushed to the rear carriage, instructing passengers to move to the front. He led a group of people to the first carriage where they manage to open the train door, climbing the emergency walkway and started walking toward the station. Luckily for them the water hadn't reach yet the walkway. However in the narrow plateform they had to walk slowly, minding each step. The fast torrent was rushing inches below their feets. Sadly a man slipped into the water and his body would be recovered only 6 days later. After the water receded, the train driver reached the safety of Shakoulu station. prompting other passengers to follow their lead. However, the walkway became unsafe with the water level rising rapidly. It discouradged a group that made it halfway toward Shakoulu station. who had to move back. They came back into the train, shut the doors and hoped for the best. They saw water streaming past train. Some were dialing with emergency numbers to call rescues via friends or family. But no response. The city's emergency call center had only 11 staff members on duty that evening struggling to respond to the scale of the disaster. Water in train reached the knees of passengers, then the waist, and soon neck deep. The power went out, the atmosphere descended. The blue light of emergency only added to their feelings of despair.Some screamed for help while other sent farewell messages to their loved ones. At 9 : 00 pm all the passengers of the train were packed in the 3 carriages in the front. Yet even there the water reached their chest.
Outside the trian, the water level were already passed their heads, virtually submerging the train underwater. Soon it would fill the carriages to the roof. Outside of this there was also the fear of suffocation. Due to the ring water, oxygen level inside the carriage dropped to the point that passengers started showing signs of hypoxia. In front of a seemingly hopeless situation, people started to try desperate measures. One passenger, gripped by panic, tried to break the glass door. Other restrained him. Had he succedeed, water from the outside would have flooded the carriage within seconds. Luckily the passengers got a break when the flood outside reached their highest point and stabilized, seemingly halting the relentless rise inside. Additionally the amoutn of pressure from water caused the train to derail and tiltly, causing one side to raise higher than the other. Passengers realized that breaking the window in the top could ventilate the cabin. 4 hours after the train stalled from the tracks, help finally arrived.
The in-depth story of the Zhengzhou Metro Line 5 Flooding Disaster 2021. A subway ride home quickly turns into a nightmare when over five hundred passengers get trapped in a flooded tunnel between two stations.
But how could such a life-threatening situation possibly unfold on a routine subway commute? Why was there no emergency response? And was this a natural disaster or a man-made catastrophe after all? Late July 2021 in China in Zhengzhou, Henan there was a storm and flooding that pushed the city's infrastructure beyond it's breaking point. It peaked on 20th July. In afternoon, rainfaill rates spiked over 8 inches per hour. Streets transformed into gushing river with water being 3 feets deep in some areas. Residents were trapped in work places or vehicles. Only to return home was by subway. However concerns grew whether subway system could handle such flooding from above the ground. The subway system was engineered to whistand flood by by sealing off impacted stations while keeping other sections oeprationnal. But as the day progressed, wate rbegan breaching overpowering pumping capabilities at multiple stations and causing power outages. The unrivaled downpour overpowered the whole system. In 4 pm when rainfall reached its maximum, subway authorities decided to close the stations most threatened by the flood, keeping the rest of the subway operationnal. Among the lines still functionning there was the line 5, the busiest of the entire system and accounting for 30% of the traffic of the entire system. City officials didn't want to prevent ten of thousands to reach their home. On 4 : 50 pm, scores of commuters boarded train number 0501 line at the Jingkai Center Square station. relieved to have caught the ride and no one knew they would embark on a disastrous trip. On 5 : 21 pm, emergency brake system suddently stopped the train. The system was triggered for unknown reason.
After a couple of minutes, the driver restarted it and continued down the track. At 5 : 40 pm, the train reached Haitansi station stopping several minutes, allowing passengers to disembark and others to board. After it, it resumed its journay to the next station, the Shakoulu station. 2 minutes later, the train stopped because of the emergency brake system. However it was for a good reason and water started going down the tracks. Unable to reach the next station, the driver attempted to reverse course and returned the train to the safety of Haitansi station. But after making 300 meters, the train was again stopped by the emergency brake system. Now it was stuck unable to go forward or back. What was strange was the amout of water coming from the Shakoulu station. Even if there was a bleach allowing water inside, standard protocols should ahve triggeredits immediate closure, sealing it to prevent the inflow. But in fact the water was coming from another source. 5 kilometers away from Shakoulou station, water had been pilling up around the Wulongkou parking lot for train operating on line 5. Because it was built on a lower Ling arena, the train lot was encircled by retaining wall to protect it from flooding. However the quality of the wall was inadequate to withstand the amount of rainfall. As the pressure increased, the wall gave away and let a torrent of water pour into the lot. From there it flowed through the subway tunnel downhill past Shakoulu and toward the track section where train number 0501 was trapped. Inside the train, 500 commuters. Water started to breach into the sixth carriage and quickly reached the ankles of passengers trapped in the upward slope leading to the Shaloulu station.
At 6 : 30 pm, aware of the unfolding situation, the train driver rushed to the rear carriage, instructing passengers to move to the front. He led a group of people to the first carriage where they manage to open the train door, climbing the emergency walkway and started walking toward the station. Luckily for them the water hadn't reach yet the walkway. However in the narrow plateform they had to walk slowly, minding each step. The fast torrent was rushing inches below their feets. Sadly a man slipped into the water and his body would be recovered only 6 days later. After the water receded, the train driver reached the safety of Shakoulu station. prompting other passengers to follow their lead. However, the walkway became unsafe with the water level rising rapidly. It discouradged a group that made it halfway toward Shakoulu station. who had to move back. They came back into the train, shut the doors and hoped for the best. They saw water streaming past train. Some were dialing with emergency numbers to call rescues via friends or family. But no response. The city's emergency call center had only 11 staff members on duty that evening struggling to respond to the scale of the disaster. Water in train reached the knees of passengers, then the waist, and soon neck deep. The power went out, the atmosphere descended. The blue light of emergency only added to their feelings of despair.Some screamed for help while other sent farewell messages to their loved ones. At 9 : 00 pm all the passengers of the train were packed in the 3 carriages in the front. Yet even there the water reached their chest.
Outside the trian, the water level were already passed their heads, virtually submerging the train underwater. Soon it would fill the carriages to the roof. Outside of this there was also the fear of suffocation. Due to the ring water, oxygen level inside the carriage dropped to the point that passengers started showing signs of hypoxia. In front of a seemingly hopeless situation, people started to try desperate measures. One passenger, gripped by panic, tried to break the glass door. Other restrained him. Had he succedeed, water from the outside would have flooded the carriage within seconds. Luckily the passengers got a break when the flood outside reached their highest point and stabilized, seemingly halting the relentless rise inside. Additionally the amoutn of pressure from water caused the train to derail and tiltly, causing one side to raise higher than the other. Passengers realized that breaking the window in the top could ventilate the cabin. 4 hours after the train stalled from the tracks, help finally arrived.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

Falling off Mount Fuji on Live Stream
Tetshu Shiohara was a lost soul living on Shikoru, in an appartment alone. He was a wandering man according to some while other describe him as humble and determined. His father was a loacl professor. Tetshu studied in America, returned to Japan but failed his attempts to pass his bar exam. These problems caused him to become more reclusive despite already having a distant relationship with his family and no friends. His lack of social interactions is probably the reason why he began live streaming in 2015. Aroudn this time Tstshu was a hobby and he announced his intention to compete in biathlon. Despite his struggling situation he didn't complain about it during his streams. He liked speaking with his viewers and was generous with his time. Among those viewers, one standed out, a women who broadcasted lifestyle videos. She was friendly with him and the 2 would interact online. He accepted an offer in 2017 to climb Mout Fuji with her. It's unclear if tfter that the 2 met again. But she encouraged him to keep climbing. Tetshu also broadcasted his daily activities including commuting to his hospital appointments. As a stage 4 colon cancer patient, he only had 7% survival odds. He was unemployed anr received financial support from his parents. He would eventually meet his fate on October 2019. He became a regular climber of Japan's tallest mountain. He reached its summit every summer season. The legend say the spirit goddess of Sakuya Hime protects and lives on the mountain. Discussions online even suggests the goddess took notice of Tetshu's presence in the events to come.Weather conditions and its popular trails make it one of the most visited mountain in the world generally between July and September. Climbing outside this window without permission of authorities is forbidden since ice and slopes make climbing its slopes dangerous for professionals let alone general public.
Generally speaking this moutain is still welcoming to beginners. Its trails have 10 rest points for climbers to sleep, get food and access first aid stations. Despite this, some accidents can happen and aroud 10 fatalities happen each year. The moutain huts only offer short term protection making sudden wealth, hypothermia, dangerous. Even in the summer months, temperatures in the summit can be beyond freezing. Always triple check the weather, listen to the locals and over prepare. The official mountain website is stating these risks. Tetshu would climb this moutain several times for at least 4 years without incident and the summer conditions mean he hd no winter climbing experience. He broadcaste his commute home from a hospital appointment and a live stream viewer metionned they would like to see the view of Mount Fuji in winter Tetshu replied that it wouldn't probably be that cold, that he would go without dying. The fact that he mentionned the word die shows he knew how dangerous it could be. Maybe he didn't care or was denial. He wouldn't have access to mountian huts for food or rest after the fifth station since it was closed. Only approved climbers are allowed to reach that summit in off season. Crampons who have solid grip are required, poles with snow basket also, and finally cie axe is essential to perform a life saving maneuver. It's, without ropes, the only way to stop an uncontrolled slip. Tetshu sent off in Tokyo on October 28th 2019. then joined the most popular Yoshida trail, planning to start hiking in mid morning to reach summit as quickly as possible and then descend the mountain during the same day. He posts that he feels sick and want to go home. At 10 : 30 he reaches the fifth station and starts his live broadcast.His gloves are not wind or waterproof. His choice of casual jeans light hiking boots and a fleece jacket aren't much better.
At 10 : 42 he enters the Yushi trail ignoring clear warmings that it's closed, air is misty and clouds hang low in the atmosphere. The terrain is a moist and dramp. Tetshu then decides to reduce the typical round trip from 10 hours to 6 hours by completing a rapid climb of the mountain. it was a tight timing and he knew he would return in darkness.Why not bringing a head or handheld torch in case? He planned to rely on his phone. He mentions how he should avoid areas of snow because he is inexperienced, he mentions that he will try to not die, that even if he dies, he won't know. Tetshu climbs over another warning sign and keep going toward the snowcapped mountain. He also admits he forgot the crampons. Shortly after he reaches the sisth station and sees that mountian huts are closed then he tells to his viewers that outside of mountain climbing, snow is the only thing easy to climb. He is also behind his schedule. Reaching the summit by 2 pm is crucial otherwise he won't be able to walk from the fifth station to the bus in darkness. Instead it will be a descent on icy slopes in pitch black with only a phone torch to guide his path. He reaches the 7th station at 11 : 35 and hears someone's voice. After he comes across a man and women on trail. Now he is 1 000 meters from the summit. Only 5 hours of sunlight left. No time for food or to rest. Mountainners can burn 700 calories per hour, even a bit more in extreme conditions. He tlels his viewers it would be better if it was snowing as he would go faster. By 1 : 19 om, Tetshu reaches the 8th station. He is completly alone and the trail is covered with snow. From here the mountain looks increasingly like a skiing resort. Guard rail and ropeways are covered by several feets of snow. At 01 : 50 pm; the trail is almost unwalkable without the right gear. Tetshu starts suffering from the lack of oxygen and stronger winds.
The frozen snow created a narrow walkable path. One wrong step would make him in serious trouble. How Tetshu would ever descent the mountain is still unclear. In 2 : 15 pm, Tetshu is walkign 30 degree slopes at least, battling the wind and starting to lose the feelings in his fingers. It's also uncealr if he is on the right path. After a few minutes he reaches the path aroud the summit. He made it before 3 pm, a hollow victory. He ignores his last chance to call for help at the final station on his route. Tetshu had to climb over frozen sbnow drifts with only lose rocks now to stay He pauses to take a photo despite having freezing fingers and nearly falling twice. He is beyond the safety of the ropeway. Then he slipped near the summit around 2 : 30 pm, the stream was still live, shutting off when the phone hit a rock. There was nothing to hold on and he didn't know how to stop a slide. So he picked up speed until he fall from one of the mountain's edge. Members of the stream contacted the police. Team of rescue and helicopters searched for 2 days. At 1 : 40 pm of 20th October 2019, a body was found just below the 7th station, the lower half of the body was missing, face too damage to recognize him and a backpack with nothing to knowhis identity. The police suspected it was Tetshu Shiohara. 13 later their hunch was confirmed. Tetshu has falle 2 300 feets or 700 meters There are still debate about his true intentions, if it was deliberate suicide or just an accident. Tetshu was a guy in search for motivation and meaning. Streams were a rare place he could find connection and recognition.
Tetshu Shiohara was a lost soul living on Shikoru, in an appartment alone. He was a wandering man according to some while other describe him as humble and determined. His father was a loacl professor. Tetshu studied in America, returned to Japan but failed his attempts to pass his bar exam. These problems caused him to become more reclusive despite already having a distant relationship with his family and no friends. His lack of social interactions is probably the reason why he began live streaming in 2015. Aroudn this time Tstshu was a hobby and he announced his intention to compete in biathlon. Despite his struggling situation he didn't complain about it during his streams. He liked speaking with his viewers and was generous with his time. Among those viewers, one standed out, a women who broadcasted lifestyle videos. She was friendly with him and the 2 would interact online. He accepted an offer in 2017 to climb Mout Fuji with her. It's unclear if tfter that the 2 met again. But she encouraged him to keep climbing. Tetshu also broadcasted his daily activities including commuting to his hospital appointments. As a stage 4 colon cancer patient, he only had 7% survival odds. He was unemployed anr received financial support from his parents. He would eventually meet his fate on October 2019. He became a regular climber of Japan's tallest mountain. He reached its summit every summer season. The legend say the spirit goddess of Sakuya Hime protects and lives on the mountain. Discussions online even suggests the goddess took notice of Tetshu's presence in the events to come.Weather conditions and its popular trails make it one of the most visited mountain in the world generally between July and September. Climbing outside this window without permission of authorities is forbidden since ice and slopes make climbing its slopes dangerous for professionals let alone general public.
Generally speaking this moutain is still welcoming to beginners. Its trails have 10 rest points for climbers to sleep, get food and access first aid stations. Despite this, some accidents can happen and aroud 10 fatalities happen each year. The moutain huts only offer short term protection making sudden wealth, hypothermia, dangerous. Even in the summer months, temperatures in the summit can be beyond freezing. Always triple check the weather, listen to the locals and over prepare. The official mountain website is stating these risks. Tetshu would climb this moutain several times for at least 4 years without incident and the summer conditions mean he hd no winter climbing experience. He broadcaste his commute home from a hospital appointment and a live stream viewer metionned they would like to see the view of Mount Fuji in winter Tetshu replied that it wouldn't probably be that cold, that he would go without dying. The fact that he mentionned the word die shows he knew how dangerous it could be. Maybe he didn't care or was denial. He wouldn't have access to mountian huts for food or rest after the fifth station since it was closed. Only approved climbers are allowed to reach that summit in off season. Crampons who have solid grip are required, poles with snow basket also, and finally cie axe is essential to perform a life saving maneuver. It's, without ropes, the only way to stop an uncontrolled slip. Tetshu sent off in Tokyo on October 28th 2019. then joined the most popular Yoshida trail, planning to start hiking in mid morning to reach summit as quickly as possible and then descend the mountain during the same day. He posts that he feels sick and want to go home. At 10 : 30 he reaches the fifth station and starts his live broadcast.His gloves are not wind or waterproof. His choice of casual jeans light hiking boots and a fleece jacket aren't much better.
At 10 : 42 he enters the Yushi trail ignoring clear warmings that it's closed, air is misty and clouds hang low in the atmosphere. The terrain is a moist and dramp. Tetshu then decides to reduce the typical round trip from 10 hours to 6 hours by completing a rapid climb of the mountain. it was a tight timing and he knew he would return in darkness.Why not bringing a head or handheld torch in case? He planned to rely on his phone. He mentions how he should avoid areas of snow because he is inexperienced, he mentions that he will try to not die, that even if he dies, he won't know. Tetshu climbs over another warning sign and keep going toward the snowcapped mountain. He also admits he forgot the crampons. Shortly after he reaches the sisth station and sees that mountian huts are closed then he tells to his viewers that outside of mountain climbing, snow is the only thing easy to climb. He is also behind his schedule. Reaching the summit by 2 pm is crucial otherwise he won't be able to walk from the fifth station to the bus in darkness. Instead it will be a descent on icy slopes in pitch black with only a phone torch to guide his path. He reaches the 7th station at 11 : 35 and hears someone's voice. After he comes across a man and women on trail. Now he is 1 000 meters from the summit. Only 5 hours of sunlight left. No time for food or to rest. Mountainners can burn 700 calories per hour, even a bit more in extreme conditions. He tlels his viewers it would be better if it was snowing as he would go faster. By 1 : 19 om, Tetshu reaches the 8th station. He is completly alone and the trail is covered with snow. From here the mountain looks increasingly like a skiing resort. Guard rail and ropeways are covered by several feets of snow. At 01 : 50 pm; the trail is almost unwalkable without the right gear. Tetshu starts suffering from the lack of oxygen and stronger winds.
The frozen snow created a narrow walkable path. One wrong step would make him in serious trouble. How Tetshu would ever descent the mountain is still unclear. In 2 : 15 pm, Tetshu is walkign 30 degree slopes at least, battling the wind and starting to lose the feelings in his fingers. It's also uncealr if he is on the right path. After a few minutes he reaches the path aroud the summit. He made it before 3 pm, a hollow victory. He ignores his last chance to call for help at the final station on his route. Tetshu had to climb over frozen sbnow drifts with only lose rocks now to stay He pauses to take a photo despite having freezing fingers and nearly falling twice. He is beyond the safety of the ropeway. Then he slipped near the summit around 2 : 30 pm, the stream was still live, shutting off when the phone hit a rock. There was nothing to hold on and he didn't know how to stop a slide. So he picked up speed until he fall from one of the mountain's edge. Members of the stream contacted the police. Team of rescue and helicopters searched for 2 days. At 1 : 40 pm of 20th October 2019, a body was found just below the 7th station, the lower half of the body was missing, face too damage to recognize him and a backpack with nothing to knowhis identity. The police suspected it was Tetshu Shiohara. 13 later their hunch was confirmed. Tetshu has falle 2 300 feets or 700 meters There are still debate about his true intentions, if it was deliberate suicide or just an accident. Tetshu was a guy in search for motivation and meaning. Streams were a rare place he could find connection and recognition.
il y a 8 mois
Little had changed for residents of the Ecuadorian Amazon over the past centuries. The indigenous tribes live the same way their forefathers did - in harmony with nature. The rainforest provides everything needed: water, food, and shelter. However, in the early 1960s, development came to their doorstep. Besides being abundant with wildlife, the Amazon was also rich in oil. This caught the attention of one of the largest oil-producing companies in the world - Texaco.
In the following three decades, the once pristine rainforest was transformed into what has been described as “one of the world’s most contaminated industrial sites” - the "Amazon's Chernobyl”... Oil waste has polluted everything from land to water to air to this day tribes living in the area are condemned to eat drink and breed the poison Texico had left behind. For 18 years affected communities fought the oil Giant in a fierce legal battle that ended differently than you'd expect. The story began in 1964 when the first oil exploration operations started in Northeast Ecuador. By that time the United States oil consumption largely overpassed domestic production and the Americans had to resort to looking abroad the U. S. Based Oil Company Texaco organized the exploration which resulted in the Striking oil in 1967. The full-scale production began five years later in return for giving the concession Ecuador's government received a 25 stake in the Consortium . Over the years the shares increased the operations were run exclusively by Texaco staff. Founded in 1902 Texaco was one of the so-called Seven Sisters companies that dominated the global petroleum industry in post-world War II era. They had tremendous experience in the business and in oil production technology moreover Texaco was one of the Pioneers in creating Advanced Environmental Protection Technologies. As required by the high pollution standards in the United States of America, drilling for oil was impossible without following the procedure to protect the environment adequately when creating an oil well. When creating an oil well in the United States, engineers would dig a temporary pit in the ground to store oil. Waste pits would be lined with a special impermeable industrial tarp to ensure no waste leaks into the ground. There was also a separation station where the crude oil was refined from its toxic residue also known as produced water. This was pumped back into the underground pockets from which the oil was initially extracted. When the drilling was completed the well-in separation station were removed, temporary pits were emptied and the oil sludge was disposed of into special containers. Then the pit would be refilled with dirt and the location would return to its original state. his was not the case in Ecuador. Instead, the Texaco management estimated that the re-injection of produced water and removal of oil waste from temporary pits were unnecessary expenses. So rather than pumping the produced water back into the ground they decided to drain it straight into nearby rivers and streams oil sludge was poured into temporary pits without protective tarp liners the that allowed the toxic waste to seep into the ground in underground water systems that local inhabitants used for drinking. Over many years of drilling operations the temporary pits were transformed into permanent ones. They had overflow pipes installed to transport the sludge into rivers and streams additionally Texaco engineers burned off the toxic natural gas during the oil extraction thus releasing enormous amounts of Highly poisonous dioxins into the air.
During the 28 years when Texaco was mining oil in the area they dumped more than 18.5 billion gallons of toxic produced water into the rainforest ( or 28 000 pools ). The waste was spilled on an area of 1 500 square miles roughly the size of the State of Rhode Island. In fact no plans were ever developed to clear the pits. The company kept all its records of environmental incidents in Ecuador such as oil leaks and waste spills under wraps. The consequences of the contaminated soil groundwater and surface waterways deeply affected the lives of tens of thousands of residents. Laboratory results showed that soil and water samples near texaco's oil wells contained high quantities of total petroleum hydrocarbons, a highly cancerous mixture of chemical compounds originating from crude oil. The amounts were up to one thousand times larger than Allowed by Ecuadorian law and even 10 000 times larger than the limits prescribed by the U. S law. Livestock were dying due to the drinking from contaminated rivers and streams fishing was made impossible because toxins in waterways killed all the fish. In the region which flourished with biodiversity, pollution decimated the wildlife. The most affected were the people who lived in the provinces of Sukumbios, Orellana, Napo and Fastaza. Exposure to high amounts of tph caused them to suffer from damaged internal organs respiratory, problems blood, poisoning stomach, skin irritation and birth defects. In addition several scientific Studies have reported increased rates of cancer children's leukemia and miscarriages in these provinces much higher than in other parts of Ecuador. For the sake of profit Texaco generated one of the worst environmental disasters in recent history. Their savings were estimated at slightly over three dollars per barrel. In 1992 texaco's concession on oil drilling operations in Ecuador ended leaving the government-owned Petro Ecuador as the business's sole owner. Unfortunately the waste they left behind continued killing the people. The following year, thirty thousand locals organize themselves into the Amazon defense front or FDA. The group worked with american-based attorney Stephen donzinger to file a class-action lawsuit against Texaco in the United States. The FDA demanded the company repair the damage it caused to the environment and financially compensate the affected communities. However they also wanted to make sure the world heard about the tragedy thus in 1993 donzinger and the fda's legal team filed a class-action lawsuit against Texaco in New York federal court. If the FDA had won the trial it would have been a precedent for other cases worldwide where the oil company had been accused of destroying the environment. A battle between David and Goliath began instead often outside the bounds of the legal system will the FDA activists gathered piles of evidence showing the extent of the crime committed in the Amazon rainforest. Texaco management developed a different strategy. They organized a lobbying campaign to to move the trial from the United States to Ecuador since winning abroad was expected to be much easier than facing an American Jury. Texaco's lawyers and experts filed 14 sworn affidavits praising the justices and fairness of the Ecuadorian courts the case they claimed belonged to Ecuador. In October 2000 Texaco was acquired by another oil giant Chevron the new management admitted Texaco dumped produced water into Amazon waterways but paradoxically continued defending that cleaning the area was not their responsibility.
Chevron's attorneys claimed the company had done its part in repairing the damage and that the rest of the duty was on the Ecuadorian government. However the company's 40 million dollar cleaning campaign was nothing more than a cosmetic treatment. In reality they only took responsibility for a small number of pits and these were just covered with dirt without removing the toxic oil sludge. While chevron's workers were hiding the traces of their misdeed its lawyers and lobbyists continued campaigning to move the trial to Ecuador. Finally, after years of lobbying the money invested paid off in 2002 the federal court in New York approved the transfer of the trial to Ecuador Chevron promised to oblige all of the decisions of its courts but the oil company was in for a surprise. The Ecuadorian Court was indeed fair-minded and impartial leading the process meticulously and taking into account the interests of both parties. The trial records accounted to 220 000 Pages . The crucial evidence were 54 Court supervised inspections of texaco's former oil wells. It was during these inspections that a shocking amount of tph was found in the water and soil. Prior to this chevron's Engineers secretly surveyed the oil wells to find areas in the ground with as little tph as possible. Nine years after the trial was moved to Ecuador the court finally reached a verdict Chevron was found guilty of polluting 2 million Acres of the Amazonian rainforest.
The court ordered them to pay 18 billion dollars for the remediation of the environment the restoration of ecology and to compensate the five affected indigenous communities. Half of the sum was the fine for Chevron refusing to publicly apologize. However, after an appeals court ruled there was no legal basis to sanction Chevron for not apologizing the fine was reduced to 9. 5 billion dollars.The verdict was the end of a long-lasting struggle to hold the Reckless Oil Company accountable. Justice was achieved it was not how Chevron saw things though much to the Public's dismay. Chevron refused to pay any fine altogether. Instead they responded to the verdict with a fierce campaign against enforcing it intending to dismiss the validity of the Ecuadorian court judgment. They filed a countersuit in the United States federal court and the hague's permanent Court of arbitration The counter suit based on the testimony of an Ecuadorian ex-judge Alberto Guerra who claimed local tribes offered him money to ghost ride the Ecuadorian court judgment. Chevron eventually left Ecuador. But the end of the day, the indigenous tribe will have to pay the price by eating and drinking toxic waste for the rest of their lives.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

The Kaprun Alpine Railway Disaster 2000
November 11, 2000, tragedy happened at the Alpine village of Kaprun when his funiculair caught fire. It had 161 passengers. it was supposed to get them to the slopes of Kitzsteinhorn. It was on 9 am. The trip shouldn't make it more than 10 minutes but instead in the funnel, it caught fire. 20 minutes after it disappeared in the tunnel, clouds of thick black smoke were billowing out of the tunnel's upper end into the Alpicenter station. Ultimatly 12 passengers defied their instincts to escape the fire. An accident that was caused by a deadly detail. The possibility of a fire breaking out in the tunnel was close to 0. Never in the Austrian cableway there was an accident like this. Nothing apparently in the tunnel or funicular incited the blaze. The Gletschernahn funicular had no engine, fuel tanks, or other part of standard railway. Using steel cables, 2 trains travelling in opposite directions are hauled by a powerful motorized winch system. Austria had 12 of these railways. This Kaprun one was built in 1974 and modernized in 1993. The single track was 3 900 meters long, of which 3 300 meters were on the tunnel. When 2 trains go to opposite directions, they bypass each other in the passing loop. Both trains comprised 2 carriages with weight compartiments accomodating up to 180 passengers. 2 cabins were positionned on either side for conductors responsible for opening and closing the doors. Most of the guests caught in that accident are used to this and travelled with the funicular many times before. Thomas Kraus, a passenger in the rearmost compartiment was the first to notice something. After only 20 meters up the track he saw control dashboard smoking in the empty conductor cabin behind him. As the train kept ascending, the smoke became more intense and then appeared in the passenger compartiment. The anxiety turned into panic when the train entered the tunnel. The passengers banged on compartiment walls. There was no way to alert the conductor in the cabin on the other end of the train. The funicular was not equipped with fire alarms, intercom systems or emergency brakes. One passenger tried to use his mobil phone to call the service station. But there was no signal inside the tunnel. The train kept going deeper inside the tunnel. The fire broke out and spread across tha vacant conductor's cabin at the back. 600 meters inside the tunnel, the trian stopped. The passengers assumed the conductor spotted the fire and stopped to evacuate but it was not the case. The conductor was confused about the train coming to an halt and the conductor didn't open the doors. The spreading fire burned the lines of the hydrualic brake system which engaged the brakes automatically. The system desigend th prevent the disaster paradoxically put the passengers into a deadly trap. The passengers in the rearmost compartiment started for a way out. But no way to open doors. Erwin Goetz, a buidler, started to hit windows with aki pole but windows were made of break resistant acrylic material. He hit as hard as he could and managed finally to make a crack in the window. But Goetz discovered another layer of acrylic glass. Several passengers already apssed out after inhaling smoke. Eventually the window broke and people started to escape the burning train. After 4 minutes the conductor finally realized what happened and called service station. He was instructed to open doors but after that, the connection was lost. The hydraulic system for opening the doors also failed. It was a matter of time ebfore the fire engulfed the whole train. Luckily the conductor was calm enough to leave his cabin and engage the door's manual lock. A moment of relief. If passengers didn't make one mistake, worse disaster could have been avoided. In the pitch black darkness with ski shoes on, the passengers tried to move away from the fire so they climbed uphill. As they struggled to move through the tunnel, they didn't notice that all the smoke was going into the direction. Kaprun's tunnel 30 degrees steep angle created a chimney effect which caused all the heat and smoke to travel upwards. None of the passengers going up survived. Too many smoke and carbon monoxyde. The majority didn't make it more than 15 meters off the train. A group of 12 passagers from the rearmost compartiment escaped the inferno because Thorsten Graedler, one of the passenger, was a volunteer firefighter. " I know fireplaces. When you open the flue, the fire shoots upwards, so you have to go down. " Hold each other's hands, believe me, we have to go down. " The passed the burning conductor's cabin and reached the smoke free zone below the train. But the agony didn't end for the group. They had to cross 600 meters of track inside the funnel. With the fire raging there was a risk that the haulage cable might snap and send the train down on them. But it didn't happen. The remaining 150 people including the conductor died from suffocation from headinw upwards. But 5 more people died because inside the twin train coming in the opposite direction, there were 2 people, a conductor and a passenger. Both didn't escape. The smoke spread and reached the Alpicenter of the summit here the staff tried to recover the power. They raised the alarm inside the station upon seeing the smoke. To save their lives, the employees left the emergency door wide open, increasing the chimney effect in the tunnel. 500 firefighters, 22 helicopters and 100 rescue vehicles came here. 4 staff members were left inside, unconscious because of the smoke. The firefighters took them out but 3 of them died. Most of casualties were tourists from Austria and Germany. Other were from USA, Japan, Czech, UK, Netherlands and Slovenia. Among the victime there was the world champion freestyle skier Sandra Schmidt. and seven time olympic medalist Josef Schaupper. 4 days after the accident, the examining judge of Salzburg court appointed Anthon Muhr to investigate it. Ministry of interior sent an unit from the KTZ forensic center to investigate. But the subject of investigation has brunt entirely. So they used the twin train to determine the source of the fire. They based their research on Thomas Kraus's testimonywho came that the smoke came from the dashboard at the conductor's cabin at the rear end of the train. Upon inspection it was determined that the only item who could have caused fire was was a cabin space heater. No one considered that such an irrevelant installation could end up burning out the entire train. The twin train's heater was taken to KTZ laboratories in Vienna. The investigators discovered that the heater's heating element was the fire's most likely source. They believed that it came loose, made contact with the plasting housing, and ignited it. The fire slowly spread, led by flammable materials inside the desk. It ate into the lines of the 42 US Gallon ( 160I ) hydraulic system which eventually burst. The released oil and rubber flooring fueled the blaze that spread across the cabin and later, the entire train. The fan was installed in 1993 when funicular became subjected to modernization. Salzburg public prosecutor Eva Danninger Soriat used reports filled by both Muhr and the KTZ to build the indictement against 16 people. 3 managers from Gletschenbahnen Kaprun AG, the company in charge of the funicular, 2 managing directors of the Austrian Swoboda Karosserie und Stahlbau GesmhbH that carried out the modernization and installed fan heaters in 1993. 3 employees of the German Mannesmann Rexroth AG who installed the hydraulic lines, 3 officials of the ministry of transport who had issued the railway operatig licence, 2 inspectors from the TUV technical Inspection Association who approved the train and 2 technicians and a builder who installed the emergency door at the Alpicenter. A fan like this is intended for home, not vehicles so it shouldn't have been installed in first place. The proximity of hydraulic lines increased the likehood of fire. In addition, no security features were present on the funicular and the entire design was a major oversight. Trial started in 18th June 2002. Then in 2009, Germany reported on the alleged manipulations of the process by the ministry of Interior and Salzburg Court. The focus was to put on the report and treatment on the expert Anthon Muhr. When he arrived at the scene of investigation he was denied access to the tunnel. When he entered it, investigators from KTZ already took away the evidence. Muhr only received the fan heater in March 2001, 4 months after the accident. The Salzburg court utterly negleted a 50 pages report filled by him. In this report, Muhr noted traces of hydraulic oil in the heater housing. He also foudn traces of the insulating material mineral wool that the Gletscherbahn technicians had used to stuff the cavities between the built in wooden panels. Muhr was finally the one who stressed the proximity of hydraulic lines as an essential factor in the breakout of the fire. During the defense, attorneys made persistent attacks on Muhr. At one point, the court ordered a psychatric examination since he had been diagnosed with depressive syndromes. Rest of experts still engaged in the process, and played down the findings of this report. On February 19th 2004, the process came to an end. Judge Manfred Seiss verdict opened a new chapter of the story. It was foud that the disputed heater had necessary safety marks and was installed following legal standards of the time. Neither Swoboda nor the employees setting the hydraulic lines were aware of its installation. The investigation also found out that no oil leaked from the hydraulic system.
November 11, 2000, tragedy happened at the Alpine village of Kaprun when his funiculair caught fire. It had 161 passengers. it was supposed to get them to the slopes of Kitzsteinhorn. It was on 9 am. The trip shouldn't make it more than 10 minutes but instead in the funnel, it caught fire. 20 minutes after it disappeared in the tunnel, clouds of thick black smoke were billowing out of the tunnel's upper end into the Alpicenter station. Ultimatly 12 passengers defied their instincts to escape the fire. An accident that was caused by a deadly detail. The possibility of a fire breaking out in the tunnel was close to 0. Never in the Austrian cableway there was an accident like this. Nothing apparently in the tunnel or funicular incited the blaze. The Gletschernahn funicular had no engine, fuel tanks, or other part of standard railway. Using steel cables, 2 trains travelling in opposite directions are hauled by a powerful motorized winch system. Austria had 12 of these railways. This Kaprun one was built in 1974 and modernized in 1993. The single track was 3 900 meters long, of which 3 300 meters were on the tunnel. When 2 trains go to opposite directions, they bypass each other in the passing loop. Both trains comprised 2 carriages with weight compartiments accomodating up to 180 passengers. 2 cabins were positionned on either side for conductors responsible for opening and closing the doors. Most of the guests caught in that accident are used to this and travelled with the funicular many times before. Thomas Kraus, a passenger in the rearmost compartiment was the first to notice something. After only 20 meters up the track he saw control dashboard smoking in the empty conductor cabin behind him. As the train kept ascending, the smoke became more intense and then appeared in the passenger compartiment. The anxiety turned into panic when the train entered the tunnel. The passengers banged on compartiment walls. There was no way to alert the conductor in the cabin on the other end of the train. The funicular was not equipped with fire alarms, intercom systems or emergency brakes. One passenger tried to use his mobil phone to call the service station. But there was no signal inside the tunnel. The train kept going deeper inside the tunnel. The fire broke out and spread across tha vacant conductor's cabin at the back. 600 meters inside the tunnel, the trian stopped. The passengers assumed the conductor spotted the fire and stopped to evacuate but it was not the case. The conductor was confused about the train coming to an halt and the conductor didn't open the doors. The spreading fire burned the lines of the hydrualic brake system which engaged the brakes automatically. The system desigend th prevent the disaster paradoxically put the passengers into a deadly trap. The passengers in the rearmost compartiment started for a way out. But no way to open doors. Erwin Goetz, a buidler, started to hit windows with aki pole but windows were made of break resistant acrylic material. He hit as hard as he could and managed finally to make a crack in the window. But Goetz discovered another layer of acrylic glass. Several passengers already apssed out after inhaling smoke. Eventually the window broke and people started to escape the burning train. After 4 minutes the conductor finally realized what happened and called service station. He was instructed to open doors but after that, the connection was lost. The hydraulic system for opening the doors also failed. It was a matter of time ebfore the fire engulfed the whole train. Luckily the conductor was calm enough to leave his cabin and engage the door's manual lock. A moment of relief. If passengers didn't make one mistake, worse disaster could have been avoided. In the pitch black darkness with ski shoes on, the passengers tried to move away from the fire so they climbed uphill. As they struggled to move through the tunnel, they didn't notice that all the smoke was going into the direction. Kaprun's tunnel 30 degrees steep angle created a chimney effect which caused all the heat and smoke to travel upwards. None of the passengers going up survived. Too many smoke and carbon monoxyde. The majority didn't make it more than 15 meters off the train. A group of 12 passagers from the rearmost compartiment escaped the inferno because Thorsten Graedler, one of the passenger, was a volunteer firefighter. " I know fireplaces. When you open the flue, the fire shoots upwards, so you have to go down. " Hold each other's hands, believe me, we have to go down. " The passed the burning conductor's cabin and reached the smoke free zone below the train. But the agony didn't end for the group. They had to cross 600 meters of track inside the funnel. With the fire raging there was a risk that the haulage cable might snap and send the train down on them. But it didn't happen. The remaining 150 people including the conductor died from suffocation from headinw upwards. But 5 more people died because inside the twin train coming in the opposite direction, there were 2 people, a conductor and a passenger. Both didn't escape. The smoke spread and reached the Alpicenter of the summit here the staff tried to recover the power. They raised the alarm inside the station upon seeing the smoke. To save their lives, the employees left the emergency door wide open, increasing the chimney effect in the tunnel. 500 firefighters, 22 helicopters and 100 rescue vehicles came here. 4 staff members were left inside, unconscious because of the smoke. The firefighters took them out but 3 of them died. Most of casualties were tourists from Austria and Germany. Other were from USA, Japan, Czech, UK, Netherlands and Slovenia. Among the victime there was the world champion freestyle skier Sandra Schmidt. and seven time olympic medalist Josef Schaupper. 4 days after the accident, the examining judge of Salzburg court appointed Anthon Muhr to investigate it. Ministry of interior sent an unit from the KTZ forensic center to investigate. But the subject of investigation has brunt entirely. So they used the twin train to determine the source of the fire. They based their research on Thomas Kraus's testimonywho came that the smoke came from the dashboard at the conductor's cabin at the rear end of the train. Upon inspection it was determined that the only item who could have caused fire was was a cabin space heater. No one considered that such an irrevelant installation could end up burning out the entire train. The twin train's heater was taken to KTZ laboratories in Vienna. The investigators discovered that the heater's heating element was the fire's most likely source. They believed that it came loose, made contact with the plasting housing, and ignited it. The fire slowly spread, led by flammable materials inside the desk. It ate into the lines of the 42 US Gallon ( 160I ) hydraulic system which eventually burst. The released oil and rubber flooring fueled the blaze that spread across the cabin and later, the entire train. The fan was installed in 1993 when funicular became subjected to modernization. Salzburg public prosecutor Eva Danninger Soriat used reports filled by both Muhr and the KTZ to build the indictement against 16 people. 3 managers from Gletschenbahnen Kaprun AG, the company in charge of the funicular, 2 managing directors of the Austrian Swoboda Karosserie und Stahlbau GesmhbH that carried out the modernization and installed fan heaters in 1993. 3 employees of the German Mannesmann Rexroth AG who installed the hydraulic lines, 3 officials of the ministry of transport who had issued the railway operatig licence, 2 inspectors from the TUV technical Inspection Association who approved the train and 2 technicians and a builder who installed the emergency door at the Alpicenter. A fan like this is intended for home, not vehicles so it shouldn't have been installed in first place. The proximity of hydraulic lines increased the likehood of fire. In addition, no security features were present on the funicular and the entire design was a major oversight. Trial started in 18th June 2002. Then in 2009, Germany reported on the alleged manipulations of the process by the ministry of Interior and Salzburg Court. The focus was to put on the report and treatment on the expert Anthon Muhr. When he arrived at the scene of investigation he was denied access to the tunnel. When he entered it, investigators from KTZ already took away the evidence. Muhr only received the fan heater in March 2001, 4 months after the accident. The Salzburg court utterly negleted a 50 pages report filled by him. In this report, Muhr noted traces of hydraulic oil in the heater housing. He also foudn traces of the insulating material mineral wool that the Gletscherbahn technicians had used to stuff the cavities between the built in wooden panels. Muhr was finally the one who stressed the proximity of hydraulic lines as an essential factor in the breakout of the fire. During the defense, attorneys made persistent attacks on Muhr. At one point, the court ordered a psychatric examination since he had been diagnosed with depressive syndromes. Rest of experts still engaged in the process, and played down the findings of this report. On February 19th 2004, the process came to an end. Judge Manfred Seiss verdict opened a new chapter of the story. It was foud that the disputed heater had necessary safety marks and was installed following legal standards of the time. Neither Swoboda nor the employees setting the hydraulic lines were aware of its installation. The investigation also found out that no oil leaked from the hydraulic system.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

The train was sinspected according to the schedule and Aplicenter's emergency. There were no indications or concerns that funicular railway could be dangerous. All sixteen defendants were acquitted of charges. The verdict shocked the prosecutor, families and the Austrian public. Then Gletscherbahnen Kaprun AG directors made a mistake that casted doubts. It seemed the entire trial was an orchestrated cover up. Upon receive acquittal, Gletscherbahnen Kaprun AG's management filled a lawsuit against the disputed heaters manufacturers, the German company Fakir. They didn't however cout on that the prosecutor's office in Salzburg would hand the case over to their colleagues in Germany. Si in November 2005, the Heilbronn Public Prosecutor's office took over and asked the KTI forensic institute of the state criminal investigation office in Stuttgart to renew the investigation. They were determined to do a thourough job. First they requested a fan heater from the twin train to be delivered for examination. When they received it they noted that a fastening dome of the heating element that allegedly let loose was missing. It was a beginning os shocking discoveries by the German investigators. The truth began to unravel. Next they revealed that the heater was disassembled before the installation. The front and the rear part of the heater were taken apart, mounted on a hole in the control panel and fastened back together. it meant that the safety test mask was no longer valid adn that the heater housing was violated and lost protection from liquid dropping in. Following discovery was that while observing the heater, German investigators foudn red liquid residue inside. In the Salzburg court verdict, the judge assumed it was only a reddish condensation.
The investigators sent the sample of the liquid to laboratory and it turned out that the red liquid was hydraulic oil. Highly inflammable hydraulic oil that has been banned in aircraft construction for years due to the risk of fire. Conclusion : the hydraulic lines were leaking and the flammable was dropping inside the heater housing. It then came in contact with the heating element and started the fire. Investigators from the KTZ Austrian forensic center delivered a fan from teh twin train with the heating element dent and touching the rear wall. But the element was intact and at safe distance from the plastic back wall. They concluded that during the inspiection, someone manipulated the heating element by bending it toward the rear wall of the housing. They accused their Austrian colleagues of manipulation the evidences. In 2008 they filled charges against 4 Austrian experts for manipulation of evidence. In spring of 2009 it was taken over by the linz office. After 4 months of coordinating teh decision with the responsible ministry, the Linz prosecutor discontinued alll 4 procedures. Gletscherbahnen seem to have bailed out and never recognized their blame for the disaster and tried to compensate financially. But for some of the relatives, that was not enough. A serie of regulations was passed to improve passenger's safety in these railways system. The Kaprun tunnel was sealed after the tragedy.
The Infamous Top Thrill Dragster Accident 2021 (Documentary)
It was on 15th August 2021. 44 year old Rachel Hawes has traveled from Swartz Creek Michigan to experience the gravity-defying ride. As the top thrill dragster hits its apex on its final descent a piece of metal from one of the trains on the roller coaster breaks off during mid-ride and flies towards her, hitting in the back of the head. Her father Robert Edmonds Witnesses the incident he sees what looks like a black Square flying in the air hitting his daughter as the roller coaster train returns to the station. When the top thrill dragster launched in 2003 it was the tallest and fastest roller coaster in the world. It launches 400 feet (122m) straight into the air and a 90 degree incline and a speed of 120 miles per hour (193kph) the ride then cruises to the peak before it flies straight back down with a 270 degree Corkscrew Twist on the way down. Attendance records show that the ride can serve over 900 Riders per hour through its turnstiles. According to another bystander the object that struck the woman flew like a metal disc through the air. The witness John McDermott who was standing in line for the ride with his girlfriend and six-year-old son says he was around 20 feet from her when he saw a piece of metal about the size of the palm of his hand hit the crowd and then saw the victims sink to the floor screaming in agonyDavid Vallo, a nurse, ran through the crowd towards the commotion to find her. The Park's Emergency Medical Services arrived shortly after. A statement released by her family a few days after the incident stated that she was in the ICU in critical condition with a brain injury. Following the shocking events Ohio Department of Agriculture investigators who inspect all the amusement rides in the state descended on Cedar Point. They conducted post-accident inspections fine comb thousands of maintenance reports witness reports and laboratory findings and interviewed more than 10 Cedar Point staff. It was found out that the piece of metal that hit her was an L-shaped bracket that connects to the back of the roller coaster car. Investigators explained that the bracketn roughly the size of an adult male's handn is connected to the back of the car and is intended to hover over the track or proximity flag plate, effectively communicates with the roller coaster operating system. During the descent, the bracket dislodged along with half the bolts which secured it and struck the victim in the head. According to the chief of amusement rides David Miron, the top thrill dragster was last inspected three months before the incident on May 14th and no significant issues were discovered. Because of Tyler's law which came into effect in 2017 after the tragic death of Tyler Jarrell who was flung from a ride at the Ohio State Fair all roller coasters must be inspected twice a year by at least two inspectors. The top thrilled dragster's second inspection was due in September with the park performing daily checks on the roller coaster. Following the accident the 25 million dollar ride was shut down for the rest of the 2021 season to allow for further investigations. In a report released six months after the incident Ohio Department of Agriculture investigators found insufficient evidence to find Cedar Fair entertainment company the holding company guilty of any infringements.
The lengthy 620-page report included an accident report of the ride reviews of hundreds of Maintenance records witness accounts and interviews with Cedar Point staff. According to the Department of Agriculture the investigation wasn't established to determine the cause of the accident but rather to guarantee the park followed all the laws and regulations to ensure the ride was safe. For its patrons therefore found no negligence stating the ride including the flag plate had been inspected the evening before the accident and did not find any damage. The full report noted that the bolts which were intact on the morning of the 15th failed by instantaneous overload fracture.. One had suddenly fractured between the head and the Bolt's body at some point between the earlier maintenance checks and the incident additionally interviews with the maintenance staff involved with the upkeep and operation of the track and the roller coaster listed two other instances in the months leading up to the accident where staff had replaced missing bolts on the Top Thrill Drgster. And a maintenance record from days before indicates that one worker had tightened 16 brake bolts and repaired a hitting break on August 13th the Park's manager of ride maintenance said the proximity flag plates at the back of each roller coaster train are removed and then replaced every year during the Park's off-season with reduced usage during the covid pandemic. The overhaul was scaled back in consultation with the ride's manufacturer intamin investigators however said they considered this when they found that the park had not committed any violations stating that Cedar Point had adhered to its reduced overhaul agreement.
The report concluded that Cedar Point's maintenance program for the roller coaster was perv the manufacturer's recommendations. It found that based on maintenance records staff had been actively inspecting making the necessary repairs and performing preventative maintenance to the roller coaster.A stop operation order has been imposed by the state following an inspection of the ride on August 16th one day after the incident in 2021. It listed a series of defects such as multiple loose bolts and fixed brake fins and the brake framework. Additionally numerous bolts were found to be of a different or improper grade and several mechanical issues were found pertaining to the train cars. It also found suspected damage to the ride's brake assembly the ride remained out of commission for the 2022 season followed by more bad news from Cedar Point on September 6th after 19 seasons in operation with 18 million Riders experiencing the world's first strata coaster Top Thrill Dragster.
.
The train was sinspected according to the schedule and Aplicenter's emergency. There were no indications or concerns that funicular railway could be dangerous. All sixteen defendants were acquitted of charges. The verdict shocked the prosecutor, families and the Austrian public. Then Gletscherbahnen Kaprun AG directors made a mistake that casted doubts. It seemed the entire trial was an orchestrated cover up. Upon receive acquittal, Gletscherbahnen Kaprun AG's management filled a lawsuit against the disputed heaters manufacturers, the German company Fakir. They didn't however cout on that the prosecutor's office in Salzburg would hand the case over to their colleagues in Germany. Si in November 2005, the Heilbronn Public Prosecutor's office took over and asked the KTI forensic institute of the state criminal investigation office in Stuttgart to renew the investigation. They were determined to do a thourough job. First they requested a fan heater from the twin train to be delivered for examination. When they received it they noted that a fastening dome of the heating element that allegedly let loose was missing. It was a beginning os shocking discoveries by the German investigators. The truth began to unravel. Next they revealed that the heater was disassembled before the installation. The front and the rear part of the heater were taken apart, mounted on a hole in the control panel and fastened back together. it meant that the safety test mask was no longer valid adn that the heater housing was violated and lost protection from liquid dropping in. Following discovery was that while observing the heater, German investigators foudn red liquid residue inside. In the Salzburg court verdict, the judge assumed it was only a reddish condensation.
The investigators sent the sample of the liquid to laboratory and it turned out that the red liquid was hydraulic oil. Highly inflammable hydraulic oil that has been banned in aircraft construction for years due to the risk of fire. Conclusion : the hydraulic lines were leaking and the flammable was dropping inside the heater housing. It then came in contact with the heating element and started the fire. Investigators from the KTZ Austrian forensic center delivered a fan from teh twin train with the heating element dent and touching the rear wall. But the element was intact and at safe distance from the plastic back wall. They concluded that during the inspiection, someone manipulated the heating element by bending it toward the rear wall of the housing. They accused their Austrian colleagues of manipulation the evidences. In 2008 they filled charges against 4 Austrian experts for manipulation of evidence. In spring of 2009 it was taken over by the linz office. After 4 months of coordinating teh decision with the responsible ministry, the Linz prosecutor discontinued alll 4 procedures. Gletscherbahnen seem to have bailed out and never recognized their blame for the disaster and tried to compensate financially. But for some of the relatives, that was not enough. A serie of regulations was passed to improve passenger's safety in these railways system. The Kaprun tunnel was sealed after the tragedy.
It was on 15th August 2021. 44 year old Rachel Hawes has traveled from Swartz Creek Michigan to experience the gravity-defying ride. As the top thrill dragster hits its apex on its final descent a piece of metal from one of the trains on the roller coaster breaks off during mid-ride and flies towards her, hitting in the back of the head. Her father Robert Edmonds Witnesses the incident he sees what looks like a black Square flying in the air hitting his daughter as the roller coaster train returns to the station. When the top thrill dragster launched in 2003 it was the tallest and fastest roller coaster in the world. It launches 400 feet (122m) straight into the air and a 90 degree incline and a speed of 120 miles per hour (193kph) the ride then cruises to the peak before it flies straight back down with a 270 degree Corkscrew Twist on the way down. Attendance records show that the ride can serve over 900 Riders per hour through its turnstiles. According to another bystander the object that struck the woman flew like a metal disc through the air. The witness John McDermott who was standing in line for the ride with his girlfriend and six-year-old son says he was around 20 feet from her when he saw a piece of metal about the size of the palm of his hand hit the crowd and then saw the victims sink to the floor screaming in agonyDavid Vallo, a nurse, ran through the crowd towards the commotion to find her. The Park's Emergency Medical Services arrived shortly after. A statement released by her family a few days after the incident stated that she was in the ICU in critical condition with a brain injury. Following the shocking events Ohio Department of Agriculture investigators who inspect all the amusement rides in the state descended on Cedar Point. They conducted post-accident inspections fine comb thousands of maintenance reports witness reports and laboratory findings and interviewed more than 10 Cedar Point staff. It was found out that the piece of metal that hit her was an L-shaped bracket that connects to the back of the roller coaster car. Investigators explained that the bracketn roughly the size of an adult male's handn is connected to the back of the car and is intended to hover over the track or proximity flag plate, effectively communicates with the roller coaster operating system. During the descent, the bracket dislodged along with half the bolts which secured it and struck the victim in the head. According to the chief of amusement rides David Miron, the top thrill dragster was last inspected three months before the incident on May 14th and no significant issues were discovered. Because of Tyler's law which came into effect in 2017 after the tragic death of Tyler Jarrell who was flung from a ride at the Ohio State Fair all roller coasters must be inspected twice a year by at least two inspectors. The top thrilled dragster's second inspection was due in September with the park performing daily checks on the roller coaster. Following the accident the 25 million dollar ride was shut down for the rest of the 2021 season to allow for further investigations. In a report released six months after the incident Ohio Department of Agriculture investigators found insufficient evidence to find Cedar Fair entertainment company the holding company guilty of any infringements.
The lengthy 620-page report included an accident report of the ride reviews of hundreds of Maintenance records witness accounts and interviews with Cedar Point staff. According to the Department of Agriculture the investigation wasn't established to determine the cause of the accident but rather to guarantee the park followed all the laws and regulations to ensure the ride was safe. For its patrons therefore found no negligence stating the ride including the flag plate had been inspected the evening before the accident and did not find any damage. The full report noted that the bolts which were intact on the morning of the 15th failed by instantaneous overload fracture.. One had suddenly fractured between the head and the Bolt's body at some point between the earlier maintenance checks and the incident additionally interviews with the maintenance staff involved with the upkeep and operation of the track and the roller coaster listed two other instances in the months leading up to the accident where staff had replaced missing bolts on the Top Thrill Drgster. And a maintenance record from days before indicates that one worker had tightened 16 brake bolts and repaired a hitting break on August 13th the Park's manager of ride maintenance said the proximity flag plates at the back of each roller coaster train are removed and then replaced every year during the Park's off-season with reduced usage during the covid pandemic. The overhaul was scaled back in consultation with the ride's manufacturer intamin investigators however said they considered this when they found that the park had not committed any violations stating that Cedar Point had adhered to its reduced overhaul agreement.
The report concluded that Cedar Point's maintenance program for the roller coaster was perv the manufacturer's recommendations. It found that based on maintenance records staff had been actively inspecting making the necessary repairs and performing preventative maintenance to the roller coaster.A stop operation order has been imposed by the state following an inspection of the ride on August 16th one day after the incident in 2021. It listed a series of defects such as multiple loose bolts and fixed brake fins and the brake framework. Additionally numerous bolts were found to be of a different or improper grade and several mechanical issues were found pertaining to the train cars. It also found suspected damage to the ride's brake assembly the ride remained out of commission for the 2022 season followed by more bad news from Cedar Point on September 6th after 19 seasons in operation with 18 million Riders experiencing the world's first strata coaster Top Thrill Dragster.
.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

Train Wiped Out a Town - The Lac-Mégantic Inferno 2013
The Lac Megantic Rail explosion. Freight trains pass daily a few yards away from the cafe. However the intensity of the sound indicated something was wrong with this train. Then 5 locomotives rush past at a staggering speed followed by a composition of 72 tank cars filled with crude oil grinding across the track and colliding against each other and then a powerful blast. It was on July 5th 2013. One hour before midnight, a freight train entered a station at Nantes with composition comprising 5 locomotives, 1 buffy car, a remote control car and 72 tank cars for 4 700 tons. It transported 2 160 000 gallons of crude oil from North Dakota to Irving Oil Refinery. Along its path there were 2 Canadian towns, Nantes and Lac Mégantic. Tom Harding, an experimented engineer, was operating the train. Harding parked the train on the main line. At the Nantes station another operator took over the following day. He was the only person on the train but followed the complete parking procedure. After applying the air BR system, he engaged handbrakes on all 5 locomotives, a buffer car and the first car. He then went through a brake test to check if the handbrakes alone were sufficient to hold the train. Harding also contacted hte US rail traffic control to report an engine malfunction and smoke coming from the lead locomotive Locomotiv was elft running to maintain the pressure in the air brake system. Eventually Harding called the local rail traffic controller Richard Labrie. Harding didn't realize that the engine's problem was more severe than he imagined. Some times after he left, witnesses reported sparks flying out of the exhaust. Flames came out. On 11 : 50 fire department received an emergency about a locomotive on fire.
After Montreal Maine and Atlantic took over the train everyone informed the firefighters that the train was safe. At 1 : 00 am as one of the firefighers returned home however, he stopped at the railway crossing not far from the Nantes station, seeing the same train he saved from fire passing the crossing at high speed. No headlights or horn sound. 1 : 15 am, the train approached Lac Megantic travelling at 100 km per horu. The train limit here was supposed to be 16 km per hour because of a long and sharp curve. The composition of 5 lovomotives and remote control car was did pass the curve but the buffer car couldn't whistand the force and derailed it draggign along the remaining 72 cars filled with crude oil. It caused a serie of massive explosions ripping through the town. The music cafe was the closest house to the train. A few guests survived by sheer luck. Without 900 meters, the blast destroeyd everything. Orange lit fireballs light up the night rising hundreds of feets in the air. But the explosion was only a prelude. Most of the derailed tanks captured ruptured during the explosion and started leaking oil, exactly over 1,5 million of gallons set on fire and spread to the streetsof lochmagantic The fire consumed everything. At 1 : 47, train operator Harding is evacuated from his hotel in Lac Megantic. He called Richard Labrie, the traffic controller Residents ran from their houses, running through smoke and flames to save their lives. Some people jumped from the floors of their homes. 150 firefighters were dispatched It however took a whole dayto reach the center of the fire.
The derailed tanks from which oil was still leaking. They succeeded in the late hours of Sunday, July 7th. Hospitals nearby expected many injuries. However over the 2 days of fire, only 1 resident came to treat his second degrees burns. The disaster left almost no room for injured people. Either you escape the fire either you were burned alive. 47 people were killed by the explosion in the blaze. 5 bodies were never found, probably vaporized by the explosion. Half of the town was destroyed. Due to oil contamination, the remaining houses had to be demolished. 1 000 people were left homeless for a while. 26 000 gallons of oil als leaked into the chaldier river in nearby lake. Tom Harding was unaware it was his train that caused the disaster. It took one hour to discover the truth. A taxi dispatched informed Richard that it was the train who caused this. As scheduled the tanker train operated by the Montreal Maine and Atlantic Railway arrived at the Nantes station. Harding secured the train, switching on the air brake system that locked all the wheels as a precautionary measure. He also applied hand brakes on all 5 locomotives plus 2 cars in case the brake system failed. However since the train was left on a slope, he was supposed to apply hand brakes on at least twice as many tank cars. He probably didn't do this because he was the only person on duty and applying a single brake was a 3 minutes long procedure that required a lot of strenght afterward, Harding performed a required brake test to ensure the train would be held by hand brakes alone.
Unfortunatly he accidentally left the air brakes on during the test which led him to believe the handbrakes would hold the train. In any case, Harding left the lead engine running to maintain the pressure in the air brake system with the air brakes applied, there was no chance the train moved and yet it did somehow. 8 months before the accident, the locomotive had been sent to a repair shop because of the engine failure. To save time, MMA's managers repaired the engine with a part of insufficient strenght and durability. The day of disaster, the low grade part failed allowing oil to leak into the body of the turbocharger. Since the engine was left running, the oil kept accumulating and once it overheated it set the whole engine on fire. Firefighters reacted quickly and prevented the fire to spread. However to extinguish it they had to kill the engine by turning the engine off. They cut the air brake system 's air supply. Unfortunatly, track MMA maintenance employees sent to the scene were not trained operators and were unaware of the consequences of leaving a locomotive engine turned off. If operator Harding had been present he would probably have started the engine again, but his colleague assured him he wouldn't have to make the trip. After the fire being extinguished, the firefighters and the MMA's employees left the scene, convinced that everything was in order. In fact, without the engines running, the air brake system gradually lost all pressure. As a result, the train was lying on slope tracks on hand brakes. A standard measure on most railways system was to park the train on side tracks equipped with buffer stops. The MMA's guidelines allowed parking on main tracks. So, with no sufficient brakes the train carrying more than 2 million gallons of oil moved down the tracks. The tracks from Nantes to Mac Megantic was dropping 4 feet each 100 yards.
By the time it reached the curve of Lac Megantic, the train was way too fast. The disaster overall resulted from poor management systems and inadequate regulations. That's what the Federal Transportation Safety board and its 181 pages report concluded. MMA however turned the blame on its own people, Tom Hardy, Richard Labrie and Jean Demaitre, the railway traffic controller and the manager of train operations. They were arrested in 2014. Harding was accused of not applying enough hand brakes and and of parking the train on a slope. Labrie was blamed for improper inspection of the train after it caught fire. While Demaitre was accused of failing to secure the train properly. The defense based their case on claiming the accused had no proper safety training and everything they did on the night of tragedy was according to the company's regulations. The 3 were specagoats. But the residents didn't feel like it. They believed the railway's managers should have sat on the bench instead. They begged to move the tracks and the transport of hazardous cargo further from the town. But the project was too expensive. Ultimatly all the 3 accused were relieved from charges. The MMA and the Canadian Pacific Railway as the main contractors got away with it. In August 2013 the company filed for bankruptcy corruption both in Canada and USA as it lacked the assets or insurance to compensate disaster victims. Other companies sued in action lawsuit agreed to pay money into a settlement fund for victims in exchange of being moved from the case, ultimatly they paid 450 million dollars to victims and other creditors. The Canadian and USA federal authorities responded to the disaster by announcing a serie of security measures including new safety standards for cars, speed limit in ubran areas and required electronic braking systems. After a decade, the railways still refuse to implement the standards that collide with their economic interests. In the meantime, the city was rebuilt.
The Lac Megantic Rail explosion. Freight trains pass daily a few yards away from the cafe. However the intensity of the sound indicated something was wrong with this train. Then 5 locomotives rush past at a staggering speed followed by a composition of 72 tank cars filled with crude oil grinding across the track and colliding against each other and then a powerful blast. It was on July 5th 2013. One hour before midnight, a freight train entered a station at Nantes with composition comprising 5 locomotives, 1 buffy car, a remote control car and 72 tank cars for 4 700 tons. It transported 2 160 000 gallons of crude oil from North Dakota to Irving Oil Refinery. Along its path there were 2 Canadian towns, Nantes and Lac Mégantic. Tom Harding, an experimented engineer, was operating the train. Harding parked the train on the main line. At the Nantes station another operator took over the following day. He was the only person on the train but followed the complete parking procedure. After applying the air BR system, he engaged handbrakes on all 5 locomotives, a buffer car and the first car. He then went through a brake test to check if the handbrakes alone were sufficient to hold the train. Harding also contacted hte US rail traffic control to report an engine malfunction and smoke coming from the lead locomotive Locomotiv was elft running to maintain the pressure in the air brake system. Eventually Harding called the local rail traffic controller Richard Labrie. Harding didn't realize that the engine's problem was more severe than he imagined. Some times after he left, witnesses reported sparks flying out of the exhaust. Flames came out. On 11 : 50 fire department received an emergency about a locomotive on fire.
After Montreal Maine and Atlantic took over the train everyone informed the firefighters that the train was safe. At 1 : 00 am as one of the firefighers returned home however, he stopped at the railway crossing not far from the Nantes station, seeing the same train he saved from fire passing the crossing at high speed. No headlights or horn sound. 1 : 15 am, the train approached Lac Megantic travelling at 100 km per horu. The train limit here was supposed to be 16 km per hour because of a long and sharp curve. The composition of 5 lovomotives and remote control car was did pass the curve but the buffer car couldn't whistand the force and derailed it draggign along the remaining 72 cars filled with crude oil. It caused a serie of massive explosions ripping through the town. The music cafe was the closest house to the train. A few guests survived by sheer luck. Without 900 meters, the blast destroeyd everything. Orange lit fireballs light up the night rising hundreds of feets in the air. But the explosion was only a prelude. Most of the derailed tanks captured ruptured during the explosion and started leaking oil, exactly over 1,5 million of gallons set on fire and spread to the streetsof lochmagantic The fire consumed everything. At 1 : 47, train operator Harding is evacuated from his hotel in Lac Megantic. He called Richard Labrie, the traffic controller Residents ran from their houses, running through smoke and flames to save their lives. Some people jumped from the floors of their homes. 150 firefighters were dispatched It however took a whole dayto reach the center of the fire.
The derailed tanks from which oil was still leaking. They succeeded in the late hours of Sunday, July 7th. Hospitals nearby expected many injuries. However over the 2 days of fire, only 1 resident came to treat his second degrees burns. The disaster left almost no room for injured people. Either you escape the fire either you were burned alive. 47 people were killed by the explosion in the blaze. 5 bodies were never found, probably vaporized by the explosion. Half of the town was destroyed. Due to oil contamination, the remaining houses had to be demolished. 1 000 people were left homeless for a while. 26 000 gallons of oil als leaked into the chaldier river in nearby lake. Tom Harding was unaware it was his train that caused the disaster. It took one hour to discover the truth. A taxi dispatched informed Richard that it was the train who caused this. As scheduled the tanker train operated by the Montreal Maine and Atlantic Railway arrived at the Nantes station. Harding secured the train, switching on the air brake system that locked all the wheels as a precautionary measure. He also applied hand brakes on all 5 locomotives plus 2 cars in case the brake system failed. However since the train was left on a slope, he was supposed to apply hand brakes on at least twice as many tank cars. He probably didn't do this because he was the only person on duty and applying a single brake was a 3 minutes long procedure that required a lot of strenght afterward, Harding performed a required brake test to ensure the train would be held by hand brakes alone.
Unfortunatly he accidentally left the air brakes on during the test which led him to believe the handbrakes would hold the train. In any case, Harding left the lead engine running to maintain the pressure in the air brake system with the air brakes applied, there was no chance the train moved and yet it did somehow. 8 months before the accident, the locomotive had been sent to a repair shop because of the engine failure. To save time, MMA's managers repaired the engine with a part of insufficient strenght and durability. The day of disaster, the low grade part failed allowing oil to leak into the body of the turbocharger. Since the engine was left running, the oil kept accumulating and once it overheated it set the whole engine on fire. Firefighters reacted quickly and prevented the fire to spread. However to extinguish it they had to kill the engine by turning the engine off. They cut the air brake system 's air supply. Unfortunatly, track MMA maintenance employees sent to the scene were not trained operators and were unaware of the consequences of leaving a locomotive engine turned off. If operator Harding had been present he would probably have started the engine again, but his colleague assured him he wouldn't have to make the trip. After the fire being extinguished, the firefighters and the MMA's employees left the scene, convinced that everything was in order. In fact, without the engines running, the air brake system gradually lost all pressure. As a result, the train was lying on slope tracks on hand brakes. A standard measure on most railways system was to park the train on side tracks equipped with buffer stops. The MMA's guidelines allowed parking on main tracks. So, with no sufficient brakes the train carrying more than 2 million gallons of oil moved down the tracks. The tracks from Nantes to Mac Megantic was dropping 4 feet each 100 yards.
By the time it reached the curve of Lac Megantic, the train was way too fast. The disaster overall resulted from poor management systems and inadequate regulations. That's what the Federal Transportation Safety board and its 181 pages report concluded. MMA however turned the blame on its own people, Tom Hardy, Richard Labrie and Jean Demaitre, the railway traffic controller and the manager of train operations. They were arrested in 2014. Harding was accused of not applying enough hand brakes and and of parking the train on a slope. Labrie was blamed for improper inspection of the train after it caught fire. While Demaitre was accused of failing to secure the train properly. The defense based their case on claiming the accused had no proper safety training and everything they did on the night of tragedy was according to the company's regulations. The 3 were specagoats. But the residents didn't feel like it. They believed the railway's managers should have sat on the bench instead. They begged to move the tracks and the transport of hazardous cargo further from the town. But the project was too expensive. Ultimatly all the 3 accused were relieved from charges. The MMA and the Canadian Pacific Railway as the main contractors got away with it. In August 2013 the company filed for bankruptcy corruption both in Canada and USA as it lacked the assets or insurance to compensate disaster victims. Other companies sued in action lawsuit agreed to pay money into a settlement fund for victims in exchange of being moved from the case, ultimatly they paid 450 million dollars to victims and other creditors. The Canadian and USA federal authorities responded to the disaster by announcing a serie of security measures including new safety standards for cars, speed limit in ubran areas and required electronic braking systems. After a decade, the railways still refuse to implement the standards that collide with their economic interests. In the meantime, the city was rebuilt.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

The Tenerife Airport Disaster (Disaster Documentary)
Both aircarft were Boeng 747 airliners belonging to the Dutch KLM company and the PAN AM of the USA. On March 27th 1977, they crashed into each other. Out of 644 people, only 61 survived. It was in the Canary islands. Grand Canary airport was the airport for all the airliners transporting tourists from all over the world to the archipelago. But because of a terrorist attack in the airport and tensions about the island independence, they were all diverted to Los Rodeo airport on the nearby island of Tenerife. It was a smaller airport but still the best solution On March 27th 12 planes landed on the airport including 5 large airliners among which we have the 2 aircrafts involved in the accident. Panam 1736 plane came from Los Angeles while KLM flight 4805 arrived from Amsterdam. The airport had a small apron area inadequate to park all the diverted aircrafts so almost all of them parked on taxi ways instead. They used the runway for both taxis and take offs. Coordination was important. The fog descending on the airport aggraveted the situation. Panam captain didn't want to land at Los Rodeos as he wanted to stay in the air in a holding pattern and wait for Grand Canaria to reopen. He still was forced to land on the Los Rodeos airport. As soon as he received the message that the airport was reopened. The captain was ready for the take off btu the problem was that between the aircraft and the runway was the KLM boeing. He had to wait for the plane to take off first.
Jacob Van Zanten, captian of the KLM asked to the contorl tower for the permission to take off. In the same time, the panam also asked to take off. PAN AM captain had to make a 180 degrees turn to make it to he third exit, not easy maneuver for such a big aircraft on such a small area. Once the KLM was ready to take off they only neede the clearance from control tower. Control tower responded with takeoff routes instructions. MERS replaced the instructions and ended his statements by saying that they were now at takeoff. The captain then edded that they were going, to which the controller responded with :" ok " to confirm he received the message. The captain however misinterpreted it for a takeoff clearance and failed to receive the other part of the message that the controller sent to him. Controller said to be ready for takeoff, that he will calling him. All the planes at the airport used the same radio frequency to communicate with the control tower which led to signal interference. One of them was the PAN AM trasmitting the message that they were still taxing down the runway. Dutch crew failed to record this message as well. KLM captain thought he had an open way in front of way, pushed the throttles to take off. But PAN AM was still on the runway. Captain Grubs from the PAN AM missed the third taxiway exit because of the thick fog. He continued to go down the way. Controller told toe PAN AM to tell when they would leave the way as the KLM was ready to take off. Little did he knew that the KLM was already starting his way for the take off. They had no groudn radars to locate the plane on the runaway and the fog was too dense. PAN AM crew noticed the KLM only when it was reaching full speed toward them. He applied full speed to escape on the left KLM noticed the PAN AM but he was going too fast to stop so he tried to takeoff. But both planes were too close for this maneuver to succeed and they collided.
KLM was fully fueled before the takeoff with tanks full in the plane. The massive fire upon the impact killed everyone. The only survivors came from the PAN AM. All 234 passengers from KLM died + the 14 crew members. As for PAN AM, the death toll was 317 passengers and 9 crew members. The entire cockpit crew survived and some other passengers. 583 people died in total.
The Seoul Halloween Crowd Crush 2022 - What We Know
Thousands of predominantly young people have converged in Itaewon in the center of the South Korean capital of Seoul. It's the most popular party district and a tourist hot spot with many narrow streets and alleys filled with bars and restaurants. The neighborhood is served by the Itaewon metro station, and videos on social media show streams of people arriving to celebrate Halloween in the early evening.
Some social media started buzzing with people saying that district's streets were so crowded they felt unsafe. One video difficult to forget features a police officer alone and desperatly trying to control the crowd. As a known traffic area, a decent police presence was expected. But according to a policeman who was working at the Itaewon police box, there were only 22 officers at the duty. Authorities would claim there were 137. At 6 pm and half, police xere called in an attempt to prevent the tragedy to happen. Police told the first operator they would send someone to go and check out, no significant reinfocements were sent for hours. The police allegdly did not dispatch anyone in response to calls made in 9 pm onwards, the hour leading up to the crush. By final ten, the final call predict the disaster that would unfold minutes later. On the other end, the caller said that it felt like people can get crushed here. Crowd pressing from both ends of the alley made made it impossible to get out. Social medias footage shows some people desperatly trying to climb on other sides of the buildings to escape. At 10 m 28, first police ambulances, 4 exactly, were dispatched, followed by 6 more. They would take longer than expected to arrive at the clogged streets. More panic insreased. At 11 pm, 30 more ambulances were deployed. 100 disaster medical assistance teams were deployed also. A doctor, that witness devastation daily, was in chock. Desperate partygoers grabbed at a bouncer's arms and legs, begging to help them.
Others staff members in surrouding clubs, tried to carry the injured ones here to have enough spaces to eprform CPR. Countless stories spoke about the sounds of screams coming from the crowd, while 5 or 6 layers of people stacked on each other, with many already having lost consciousness. During early hours, the city governement started to receive multiple missing reports. It would take days to identify the victims. The injured were taken in the 18 hospitals that were near. South Korea's president, in reaction, has held an emergency meeting and announced an immediate investigation.
Both aircarft were Boeng 747 airliners belonging to the Dutch KLM company and the PAN AM of the USA. On March 27th 1977, they crashed into each other. Out of 644 people, only 61 survived. It was in the Canary islands. Grand Canary airport was the airport for all the airliners transporting tourists from all over the world to the archipelago. But because of a terrorist attack in the airport and tensions about the island independence, they were all diverted to Los Rodeo airport on the nearby island of Tenerife. It was a smaller airport but still the best solution On March 27th 12 planes landed on the airport including 5 large airliners among which we have the 2 aircrafts involved in the accident. Panam 1736 plane came from Los Angeles while KLM flight 4805 arrived from Amsterdam. The airport had a small apron area inadequate to park all the diverted aircrafts so almost all of them parked on taxi ways instead. They used the runway for both taxis and take offs. Coordination was important. The fog descending on the airport aggraveted the situation. Panam captain didn't want to land at Los Rodeos as he wanted to stay in the air in a holding pattern and wait for Grand Canaria to reopen. He still was forced to land on the Los Rodeos airport. As soon as he received the message that the airport was reopened. The captain was ready for the take off btu the problem was that between the aircraft and the runway was the KLM boeing. He had to wait for the plane to take off first.
Jacob Van Zanten, captian of the KLM asked to the contorl tower for the permission to take off. In the same time, the panam also asked to take off. PAN AM captain had to make a 180 degrees turn to make it to he third exit, not easy maneuver for such a big aircraft on such a small area. Once the KLM was ready to take off they only neede the clearance from control tower. Control tower responded with takeoff routes instructions. MERS replaced the instructions and ended his statements by saying that they were now at takeoff. The captain then edded that they were going, to which the controller responded with :" ok " to confirm he received the message. The captain however misinterpreted it for a takeoff clearance and failed to receive the other part of the message that the controller sent to him. Controller said to be ready for takeoff, that he will calling him. All the planes at the airport used the same radio frequency to communicate with the control tower which led to signal interference. One of them was the PAN AM trasmitting the message that they were still taxing down the runway. Dutch crew failed to record this message as well. KLM captain thought he had an open way in front of way, pushed the throttles to take off. But PAN AM was still on the runway. Captain Grubs from the PAN AM missed the third taxiway exit because of the thick fog. He continued to go down the way. Controller told toe PAN AM to tell when they would leave the way as the KLM was ready to take off. Little did he knew that the KLM was already starting his way for the take off. They had no groudn radars to locate the plane on the runaway and the fog was too dense. PAN AM crew noticed the KLM only when it was reaching full speed toward them. He applied full speed to escape on the left KLM noticed the PAN AM but he was going too fast to stop so he tried to takeoff. But both planes were too close for this maneuver to succeed and they collided.
KLM was fully fueled before the takeoff with tanks full in the plane. The massive fire upon the impact killed everyone. The only survivors came from the PAN AM. All 234 passengers from KLM died + the 14 crew members. As for PAN AM, the death toll was 317 passengers and 9 crew members. The entire cockpit crew survived and some other passengers. 583 people died in total.
Thousands of predominantly young people have converged in Itaewon in the center of the South Korean capital of Seoul. It's the most popular party district and a tourist hot spot with many narrow streets and alleys filled with bars and restaurants. The neighborhood is served by the Itaewon metro station, and videos on social media show streams of people arriving to celebrate Halloween in the early evening.
Some social media started buzzing with people saying that district's streets were so crowded they felt unsafe. One video difficult to forget features a police officer alone and desperatly trying to control the crowd. As a known traffic area, a decent police presence was expected. But according to a policeman who was working at the Itaewon police box, there were only 22 officers at the duty. Authorities would claim there were 137. At 6 pm and half, police xere called in an attempt to prevent the tragedy to happen. Police told the first operator they would send someone to go and check out, no significant reinfocements were sent for hours. The police allegdly did not dispatch anyone in response to calls made in 9 pm onwards, the hour leading up to the crush. By final ten, the final call predict the disaster that would unfold minutes later. On the other end, the caller said that it felt like people can get crushed here. Crowd pressing from both ends of the alley made made it impossible to get out. Social medias footage shows some people desperatly trying to climb on other sides of the buildings to escape. At 10 m 28, first police ambulances, 4 exactly, were dispatched, followed by 6 more. They would take longer than expected to arrive at the clogged streets. More panic insreased. At 11 pm, 30 more ambulances were deployed. 100 disaster medical assistance teams were deployed also. A doctor, that witness devastation daily, was in chock. Desperate partygoers grabbed at a bouncer's arms and legs, begging to help them.
Others staff members in surrouding clubs, tried to carry the injured ones here to have enough spaces to eprform CPR. Countless stories spoke about the sounds of screams coming from the crowd, while 5 or 6 layers of people stacked on each other, with many already having lost consciousness. During early hours, the city governement started to receive multiple missing reports. It would take days to identify the victims. The injured were taken in the 18 hospitals that were near. South Korea's president, in reaction, has held an emergency meeting and announced an immediate investigation.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

Horror At Sea - The Viking Sky Cruise Disaster
In the middle of a raging storm, a cruise ship carrying over 1000 souls loses power. The engines fail, and a huge wave shatters windows, causing freezing water to flood the decks.The Viking Sky is close to sinking. As it drifts towards rocks on the shore, its captain sends a desperate mayday call, and experts prepare for a disaster on the scale of the Titanic.This is a tale of shocking oversight, the story of how the Viking Sky cruise almost ended in catastrophe... It was on March 23rd 2019. It was sailing through Hustadvika Bay. After engine shut down it endured 6 meters tall waves for hours. Its crew tried to restart the engine. Viking Sky is one of the 6 ships owned by Viking ocean cruises. It specializes in luxury holidays where guests can enjoy scenic views ot the Arctic circle and catch glimpses of the northern lights but as an entertainment company, Viking ocean cruises doesn't have the naval expertise to maintain the fleet. Once the ships are built by italian firm Fincantieri, it's seafaring activities are handled by Wellenius Wilhemsen, a maritime service provider based in Norway. The Viking Sky is still condired a state of the art cruise liner today so when it's launched in 2017, you would think it had all the documentations in place but conflicting reports suggest that it wasn't the case. In 2016, Wellenius engineers working on a sister vessel realized that they lacked crucial information to maintain the fleet. Its engine manufacturer hadn't provided guidelines for the correct oil and alarm levels of its sum tank. Strange oversight for a 400 million ocean cruiser. but it's even more baffling as the ship's engines also generate its electricity so if they fail mid voyage, the Viking Sky would be left without power and propulsion. So for years the fleet carried thousands of passengers on ships its passengers weren't even sure how to maintain.
As if it wasn't troubling enough, the ship could carry 930 guests and 465 crew members. Despite those numbers it was classified as a small ship. In this case their route was supposed to be 12 days long, from Bergen in Norway to Tromsø, passing by Bodo and Hustadvika Bay. The region is infamous for its shallow reefs, rough seas and sudden weather changes. The first week went as expected with the guests enjoying a visit to Tromsø on 21st March 2019. But severe weather was predicted over next days and rival companies canel the plan trips but weather wasn't the only problem. In a regular incident for the fleet 1, one of its diesel electric generators ( DG 3 ), was offline due to a faulty turbocharger. But the ship would run behind schedule if it waited at Tromsø for the spare parts to arrive. The VIking Sky also had a staffing shortage with its mandatory pilots. 2 were needed to ensure passage through a more challenging section of its course. However one of the onboard pilots was only certified to sail up. Replacement pilot was set to join after the most dangerous leg of the route in Hustadvika Bay. A technician could repair the generated once once the boat reached Stavanger. Aware of the risks the left Tromsø on the evening but the decision broke maritime regulations with. With 1 offline, Viking Sky wouldn't have enough fallback generators if the other engines encountered issues. 3 hours after leaving the port, an alarm alerted the crew that DG2 generator had low lubricating oil but it stopped shortly afterwards so no further action was taken by the etchnicians. Weather was still fine. As the day progressed the crew monitored increasing wind speeds. By morning, the captian was worried aout reaching the next destination. After assessing the situation they cancelled the trip to Bodo. Disappointed, he told the passangers the area was too dangerous to sail. Instead, the Viking Sky set course to Stavanger.
Several hours later, crew was instructed to prepare the ship for deteriorating weather and secure loose items in the hall but as the ship continued to sail in mellow waters inshore, the wind and waves became increasingly restless throughout the day. By midnight the breeze had grown to galeforce winds and the ship log book recorded 6 meters waves, forcing the captian to half the ship's speed. to ensure a more cmofortable ride for passengers. In early hours of follong days, multiple warnings registered on the ship, first first indicating lw lubricating oil, this time for DG4 sump tank. When the ship entered near Trondheim, winds increased to a severe gale. Despite being sheltered from the full effects of the volatile tide by a series of islands, more alarms sounded as they crossed the Trondheim fairway, this time included a second low oil level warning for DG4. Forecast predicted the strong winds would only grow stronger. So the captain ordered a heavy weather check likst to prepare the onslaught. While this happened, 150 warnings triggered for various systems, including additional low oil alerts for DG4. At this point the enginner on watch acknowledged 3 separate warnings for DG4 but each was cleared from the system without adding oil investigate further. Meanwhile, passengers were served breakfast as usual but a feeling of unease spread as they began to feel the effects of the emergingstorm, some struggled to stay on their feets, other watched as glasses smashed and objectsslide across restaurant tables. Eventually enginners inspected tanks, manually testing the alarms and recording oil levels towards the end of the 4 noon watch. But the level s were just judged to be normal and in a few short hours, it would have serious consequences. As it approached Hustadvika Bay, the pilots left the bridge as expected.
Back in the water, the Viking Sky was rocked by 7 meters waves and the captain informed passengers that a storm was coming. 1 hour later, the weather was officially declared a violent storm. Open doors and windows swung uncontrollably against their frames as gusting winds reached 90 miles per hour. Shortly after 1 pm, the crew reported it had finished the weather check list. This included topping up the sump tanks with lubricating oil but despite marking the checks as complete, the tanks still hadn't been topped up. Due to their negligence had been running low on oil for over 24 hours. As the ship pitched and rolled in the sea air, was sucked into the lubricating system pipes, further reducing the engine's oil supply and dramatically increased their load. But a fatal design doomed the voyage from the moment it left the port. On top of being underfilled, the sump tanks were aroudn 40% smaller than the regulations required. This was the final straw for the ship's strained engines as they had reached their breaking point. In the engine control room, several alarms went off at once, DG4 oil had dipped below the minimum level, triggering automatic mechanism to prevent a blowout. Both DG4 and DG1 started loosing electrical power which was followed by a low oil alert for DG1. Despite the warnings, the enginners simply cleared them from the system. Above on the bridge, the captain and pilot relaxed, unconcerned. So when DG4 and DG2 shut down, it came as a shock. Both came by low lube oil pressure and a flurry sound of alarms sounded at once. The engineer on watch contacted the chief enginner ho quickly headed to the control room with limited speed. The Viking Sky stabilizers automatically retracted, causing the ship to roll almost double the 6 degrees angle it was before. Technicians tried to get DG2 back online.
At almost 2 pm, the DG2 was restarted by crew and ship's stablizers were brought online. But it was a temporary respire as DG2 shut down again followed by DG1, causing a total blackout. The ship had no power or steering. They were stranded dead in the water. Panic unfolded among passengers. who wondered what happened. In the control room, crew tried to deal with a poorly designed alarm system. Up to 1 000 warning sounded at once. But many of them were for minor systems clouding the enginners to what was trully wrong. Enginners couldn't estimate how long it would take to restore the power. Seeing his ship made a drifting toward shore, he made an urgent distress call. They were hundred of meters from rocks. Norwegian Coast Guard responded who launced boats the aid the ship. The Viking Sky continued drifting, damaging the anchors. as they dragged along the seafloor. The crew fought to get the engines back online. They finally realized low oil pressure was the problem and started transferring oil into the sump tanks but poor training meant they had not practiced restoring power without a back up generator. So steps to reset the engines weren't completed. One of the pilot communicated with rescuers and the captian prepared the ship for evacuation. To their credit, the passengers remained as calm as possible. Then enginners managed to reset DG2 and restore limited power to the vessel, meaning there was a chance to fire up the propeller motors. But not long after the boat drifted over a rock with 4 meters of clearance the the ship, experts later warned it was only minutes from running a ground. Half an hour later, passengers anticipated their rescue, then a massive wave hit the ship and se cond smashed windows, ripping a heavy metal door off its hinges, causing ice cold water to flood through the ship. Some were injured by shards of glass and other loose objects when doors struck passengers. There was a risk that hundred of people freezing to death.
In the middle of a raging storm, a cruise ship carrying over 1000 souls loses power. The engines fail, and a huge wave shatters windows, causing freezing water to flood the decks.The Viking Sky is close to sinking. As it drifts towards rocks on the shore, its captain sends a desperate mayday call, and experts prepare for a disaster on the scale of the Titanic.This is a tale of shocking oversight, the story of how the Viking Sky cruise almost ended in catastrophe... It was on March 23rd 2019. It was sailing through Hustadvika Bay. After engine shut down it endured 6 meters tall waves for hours. Its crew tried to restart the engine. Viking Sky is one of the 6 ships owned by Viking ocean cruises. It specializes in luxury holidays where guests can enjoy scenic views ot the Arctic circle and catch glimpses of the northern lights but as an entertainment company, Viking ocean cruises doesn't have the naval expertise to maintain the fleet. Once the ships are built by italian firm Fincantieri, it's seafaring activities are handled by Wellenius Wilhemsen, a maritime service provider based in Norway. The Viking Sky is still condired a state of the art cruise liner today so when it's launched in 2017, you would think it had all the documentations in place but conflicting reports suggest that it wasn't the case. In 2016, Wellenius engineers working on a sister vessel realized that they lacked crucial information to maintain the fleet. Its engine manufacturer hadn't provided guidelines for the correct oil and alarm levels of its sum tank. Strange oversight for a 400 million ocean cruiser. but it's even more baffling as the ship's engines also generate its electricity so if they fail mid voyage, the Viking Sky would be left without power and propulsion. So for years the fleet carried thousands of passengers on ships its passengers weren't even sure how to maintain.
As if it wasn't troubling enough, the ship could carry 930 guests and 465 crew members. Despite those numbers it was classified as a small ship. In this case their route was supposed to be 12 days long, from Bergen in Norway to Tromsø, passing by Bodo and Hustadvika Bay. The region is infamous for its shallow reefs, rough seas and sudden weather changes. The first week went as expected with the guests enjoying a visit to Tromsø on 21st March 2019. But severe weather was predicted over next days and rival companies canel the plan trips but weather wasn't the only problem. In a regular incident for the fleet 1, one of its diesel electric generators ( DG 3 ), was offline due to a faulty turbocharger. But the ship would run behind schedule if it waited at Tromsø for the spare parts to arrive. The VIking Sky also had a staffing shortage with its mandatory pilots. 2 were needed to ensure passage through a more challenging section of its course. However one of the onboard pilots was only certified to sail up. Replacement pilot was set to join after the most dangerous leg of the route in Hustadvika Bay. A technician could repair the generated once once the boat reached Stavanger. Aware of the risks the left Tromsø on the evening but the decision broke maritime regulations with. With 1 offline, Viking Sky wouldn't have enough fallback generators if the other engines encountered issues. 3 hours after leaving the port, an alarm alerted the crew that DG2 generator had low lubricating oil but it stopped shortly afterwards so no further action was taken by the etchnicians. Weather was still fine. As the day progressed the crew monitored increasing wind speeds. By morning, the captian was worried aout reaching the next destination. After assessing the situation they cancelled the trip to Bodo. Disappointed, he told the passangers the area was too dangerous to sail. Instead, the Viking Sky set course to Stavanger.
Several hours later, crew was instructed to prepare the ship for deteriorating weather and secure loose items in the hall but as the ship continued to sail in mellow waters inshore, the wind and waves became increasingly restless throughout the day. By midnight the breeze had grown to galeforce winds and the ship log book recorded 6 meters waves, forcing the captian to half the ship's speed. to ensure a more cmofortable ride for passengers. In early hours of follong days, multiple warnings registered on the ship, first first indicating lw lubricating oil, this time for DG4 sump tank. When the ship entered near Trondheim, winds increased to a severe gale. Despite being sheltered from the full effects of the volatile tide by a series of islands, more alarms sounded as they crossed the Trondheim fairway, this time included a second low oil level warning for DG4. Forecast predicted the strong winds would only grow stronger. So the captain ordered a heavy weather check likst to prepare the onslaught. While this happened, 150 warnings triggered for various systems, including additional low oil alerts for DG4. At this point the enginner on watch acknowledged 3 separate warnings for DG4 but each was cleared from the system without adding oil investigate further. Meanwhile, passengers were served breakfast as usual but a feeling of unease spread as they began to feel the effects of the emergingstorm, some struggled to stay on their feets, other watched as glasses smashed and objectsslide across restaurant tables. Eventually enginners inspected tanks, manually testing the alarms and recording oil levels towards the end of the 4 noon watch. But the level s were just judged to be normal and in a few short hours, it would have serious consequences. As it approached Hustadvika Bay, the pilots left the bridge as expected.
Back in the water, the Viking Sky was rocked by 7 meters waves and the captain informed passengers that a storm was coming. 1 hour later, the weather was officially declared a violent storm. Open doors and windows swung uncontrollably against their frames as gusting winds reached 90 miles per hour. Shortly after 1 pm, the crew reported it had finished the weather check list. This included topping up the sump tanks with lubricating oil but despite marking the checks as complete, the tanks still hadn't been topped up. Due to their negligence had been running low on oil for over 24 hours. As the ship pitched and rolled in the sea air, was sucked into the lubricating system pipes, further reducing the engine's oil supply and dramatically increased their load. But a fatal design doomed the voyage from the moment it left the port. On top of being underfilled, the sump tanks were aroudn 40% smaller than the regulations required. This was the final straw for the ship's strained engines as they had reached their breaking point. In the engine control room, several alarms went off at once, DG4 oil had dipped below the minimum level, triggering automatic mechanism to prevent a blowout. Both DG4 and DG1 started loosing electrical power which was followed by a low oil alert for DG1. Despite the warnings, the enginners simply cleared them from the system. Above on the bridge, the captain and pilot relaxed, unconcerned. So when DG4 and DG2 shut down, it came as a shock. Both came by low lube oil pressure and a flurry sound of alarms sounded at once. The engineer on watch contacted the chief enginner ho quickly headed to the control room with limited speed. The Viking Sky stabilizers automatically retracted, causing the ship to roll almost double the 6 degrees angle it was before. Technicians tried to get DG2 back online.
At almost 2 pm, the DG2 was restarted by crew and ship's stablizers were brought online. But it was a temporary respire as DG2 shut down again followed by DG1, causing a total blackout. The ship had no power or steering. They were stranded dead in the water. Panic unfolded among passengers. who wondered what happened. In the control room, crew tried to deal with a poorly designed alarm system. Up to 1 000 warning sounded at once. But many of them were for minor systems clouding the enginners to what was trully wrong. Enginners couldn't estimate how long it would take to restore the power. Seeing his ship made a drifting toward shore, he made an urgent distress call. They were hundred of meters from rocks. Norwegian Coast Guard responded who launced boats the aid the ship. The Viking Sky continued drifting, damaging the anchors. as they dragged along the seafloor. The crew fought to get the engines back online. They finally realized low oil pressure was the problem and started transferring oil into the sump tanks but poor training meant they had not practiced restoring power without a back up generator. So steps to reset the engines weren't completed. One of the pilot communicated with rescuers and the captian prepared the ship for evacuation. To their credit, the passengers remained as calm as possible. Then enginners managed to reset DG2 and restore limited power to the vessel, meaning there was a chance to fire up the propeller motors. But not long after the boat drifted over a rock with 4 meters of clearance the the ship, experts later warned it was only minutes from running a ground. Half an hour later, passengers anticipated their rescue, then a massive wave hit the ship and se cond smashed windows, ripping a heavy metal door off its hinges, causing ice cold water to flood through the ship. Some were injured by shards of glass and other loose objects when doors struck passengers. There was a risk that hundred of people freezing to death.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

The coach guards couldn't attach toe lines to stablize the ship which was listing as much as 30 degrees. With no other option, they returned ashore. The coast guards dispatched 6 helicopters to airlift passengers to air safety. They prioritized the injured and most vulnerable guests. But progression was steady and rescuers could only make it as fast as the conditions allowed. So they winched passengers 2 at times.To speed up operation, during the next hour, DG1 and DG2 wer ebrought back online. This gave the Viking Sky a slim chance to avoid the shallows. Not long after, a coast guard vessel and a heavy tugbo vivac reached the ship reached the ship of the relief of all on board, helping the captian to navigate away from the reef. Even so the ship struggled to get clear of danger entirely. So another dugboat was drafted to help but it would take some times to reach the area. As the shiip crawled to deeper waters, DG2 briefly shut down due to low oil pressure which was quickly resolved by enginners. it now had 3 generators working. The evacuation continued through the night. Early hours of March 24th, the tugboat ocean response arrived at the scene and 1 100 people were still stranded even with rescuers working non stop. The remaining passengers have been trapped for over 13 hours waiting for daylight and end this ordeal. Luckily when the sun rose, the storm began to ease. The starboard anchor was so damaged it couldn't be winched bacl into place, was cut free. And the Viking Sky limped ashore aiming for Molde. Later afternoon, everyone was saved. In the aftermath, the Viking ocean cruises reported major damage to the ship's starboard or right and windows, wome were destroyed. There was also stress in the ship's structure and superficial damage. Failure to maintain oil level and a flaw in the design were the main causes of the accident.
.
The Charles de Gaulle Airport Collapse (Disaster Documentary)
In both highly developed countries and those underachieving, public architecture is the showcase of national pride. In the early 2000s, the French proudly presented Terminal E of the Charles de Gaulle Airport in Paris - the masterpiece of Architecture. Less than a year later, it became an embarrassment on a world-scale level. But on March 23rd 2004, disaster stuck. For many people, Charles de Gaulle airport is the first image they get when coming in France. It's like the mirror of the nation. That's why Paris Aeroport group 750 million euros a new terminal for international arrivals and departures. Paul Andreu, a reknowned french architect, was hired for the job since he already designed other terminals at the same airport and many airports worldwide. When the terminal was opened in June 2003, it seemed like nothing similar was made in history. Terminator 3e with its futuristic look was a breathtaker. However the warden acrhitecture falled on March 2004, killing 4 passengers and injuring many others. After an inspection, it was revealed not only the culprits but the deficits of the entire construction scene. On morningof sunday 23rd March 2004, cleaning crew wiping floor of terminal 2E noticed a strange dust on the floor. A moment later they foudn out this was concrete dust scattering from the terminal's concrete ceiling. Cleaners reported the case to their supervisors who discovered that issues appeared on the roof. The cracks appearing meant that the concrete roof was beginning to tear away from its steel support. What airports failed to notice is that the construction already began to collapse. First an underside concrete block on the shell of the building fell then 90 minutes later the northern concrete wall buckled and the struts holding it pierced through. Finally, concrete roof lost support and the first to collapse was the ceiling's edge beam. Luckily the crowd at the terminal was far from that during peak hours.
Still passengers were arriving from South Africa and the USA and other waited for their flight to prague. The airport officials and police officers began the immediate evacuation of the terminal but it was too late. At 7 am, the concrete roof cracked and collapsed. burrying dozens of passengers under the piles of concrete. Recue teams arrived fast but there was no way to move heavy chunks of concrete. In afternoong only they brought in a heavy crane to clean the site. Police rescue teams arrived with trained dogs to search for the bodies. The weight of tons of concrete and glass ended with 4 dead passengers, 2 from China, 1 from Ukraine, another from Lebanon. Luckily the collapse happened early in the morning and not during the peak hours because it could have been a much bigger full scale tragedy. On site investigators arrived to determine the causes of the accident. A terrorist attack struck Madrid 2 months ago and the french police at first suspected that the same thing happened here. However, rpeorts from witnesses confirmed it was a structural failure. Andrew was not only the architect for the project. He was also in charge of building the first terminal of the airport between 1966 and 1974. Over time he designed several airports across the globe such as airports in Shanghai, Manilla, Abu Dhabi and Dubai. All of them are true masterpieces of airport architecture. Terminal 2E was his last airport job. Its design was unique and ambitious. It was a 450 meters long elliptical tube resting on parallel longitudinal beams. The perforated tube was built of 30 centimeters thick reinforced concrete ring. The pecularity of the structure was that there was no pillars inside to support it. Instead, Andrew applied the principles of tunnel construction by installing the outer steel frame to which concrete rings were attached via struts. This way, both the external frame and concrete rings carried the weight of the structure and decorative glass panels.
The construction looked very futuristic and spacious since there were no pillar inside to impede the free movements of passengers. It was innovative and impressive design. However it had to be built in perfect static balance to hold. The administrative investigation committee that invvestigated the accident cited 2 key facotrs leading to this. First was the structural engineering failure. The construction had design flaws. The design was on the edge of static balance. Terminal 2E lacked redundant supports, an otherwise standard construction feature added as a precaution measure in case one or more support fails.Terminal 2E had none and when the support failed, it shifted the load to other supports which ultimatly led to a collapse. The committeee also cited that the support failed in the first place because of their inadequate strenght and low resistance to temperature changes. On the day before the accident, temperatures varied from 20 to 4 degrees celsius. It was too much of a stress for the weak outer frame. The entire structure was labeled as having an inadequate capacity to resist stress. During 11 months of existence, the stress gradually weakened the structure u ntil it finally collapsed. Second factor was the process failure. The firm that built the terminal was the french company Aéroports de Paris. It was in charge of both designing and constructing the terminal, meaning there was no contrl on how the project was carried out. To cut the expenses and shorten the construction period, ADP cut some corners and circumvented essential protocols such as detailed analysis of the structure. The committee also noticed that the external support frame was chosen based on his aesthetic appeal rather than on calculating engineering judgement. Rather than consulting the construction engineers the management of the ADP increased pressure on them to finish the job earlier and at a lesser cost which led to mistakes in the construction process.
.
The coach guards couldn't attach toe lines to stablize the ship which was listing as much as 30 degrees. With no other option, they returned ashore. The coast guards dispatched 6 helicopters to airlift passengers to air safety. They prioritized the injured and most vulnerable guests. But progression was steady and rescuers could only make it as fast as the conditions allowed. So they winched passengers 2 at times.To speed up operation, during the next hour, DG1 and DG2 wer ebrought back online. This gave the Viking Sky a slim chance to avoid the shallows. Not long after, a coast guard vessel and a heavy tugbo vivac reached the ship reached the ship of the relief of all on board, helping the captian to navigate away from the reef. Even so the ship struggled to get clear of danger entirely. So another dugboat was drafted to help but it would take some times to reach the area. As the shiip crawled to deeper waters, DG2 briefly shut down due to low oil pressure which was quickly resolved by enginners. it now had 3 generators working. The evacuation continued through the night. Early hours of March 24th, the tugboat ocean response arrived at the scene and 1 100 people were still stranded even with rescuers working non stop. The remaining passengers have been trapped for over 13 hours waiting for daylight and end this ordeal. Luckily when the sun rose, the storm began to ease. The starboard anchor was so damaged it couldn't be winched bacl into place, was cut free. And the Viking Sky limped ashore aiming for Molde. Later afternoon, everyone was saved. In the aftermath, the Viking ocean cruises reported major damage to the ship's starboard or right and windows, wome were destroyed. There was also stress in the ship's structure and superficial damage. Failure to maintain oil level and a flaw in the design were the main causes of the accident.
.
In both highly developed countries and those underachieving, public architecture is the showcase of national pride. In the early 2000s, the French proudly presented Terminal E of the Charles de Gaulle Airport in Paris - the masterpiece of Architecture. Less than a year later, it became an embarrassment on a world-scale level. But on March 23rd 2004, disaster stuck. For many people, Charles de Gaulle airport is the first image they get when coming in France. It's like the mirror of the nation. That's why Paris Aeroport group 750 million euros a new terminal for international arrivals and departures. Paul Andreu, a reknowned french architect, was hired for the job since he already designed other terminals at the same airport and many airports worldwide. When the terminal was opened in June 2003, it seemed like nothing similar was made in history. Terminator 3e with its futuristic look was a breathtaker. However the warden acrhitecture falled on March 2004, killing 4 passengers and injuring many others. After an inspection, it was revealed not only the culprits but the deficits of the entire construction scene. On morningof sunday 23rd March 2004, cleaning crew wiping floor of terminal 2E noticed a strange dust on the floor. A moment later they foudn out this was concrete dust scattering from the terminal's concrete ceiling. Cleaners reported the case to their supervisors who discovered that issues appeared on the roof. The cracks appearing meant that the concrete roof was beginning to tear away from its steel support. What airports failed to notice is that the construction already began to collapse. First an underside concrete block on the shell of the building fell then 90 minutes later the northern concrete wall buckled and the struts holding it pierced through. Finally, concrete roof lost support and the first to collapse was the ceiling's edge beam. Luckily the crowd at the terminal was far from that during peak hours.
Still passengers were arriving from South Africa and the USA and other waited for their flight to prague. The airport officials and police officers began the immediate evacuation of the terminal but it was too late. At 7 am, the concrete roof cracked and collapsed. burrying dozens of passengers under the piles of concrete. Recue teams arrived fast but there was no way to move heavy chunks of concrete. In afternoong only they brought in a heavy crane to clean the site. Police rescue teams arrived with trained dogs to search for the bodies. The weight of tons of concrete and glass ended with 4 dead passengers, 2 from China, 1 from Ukraine, another from Lebanon. Luckily the collapse happened early in the morning and not during the peak hours because it could have been a much bigger full scale tragedy. On site investigators arrived to determine the causes of the accident. A terrorist attack struck Madrid 2 months ago and the french police at first suspected that the same thing happened here. However, rpeorts from witnesses confirmed it was a structural failure. Andrew was not only the architect for the project. He was also in charge of building the first terminal of the airport between 1966 and 1974. Over time he designed several airports across the globe such as airports in Shanghai, Manilla, Abu Dhabi and Dubai. All of them are true masterpieces of airport architecture. Terminal 2E was his last airport job. Its design was unique and ambitious. It was a 450 meters long elliptical tube resting on parallel longitudinal beams. The perforated tube was built of 30 centimeters thick reinforced concrete ring. The pecularity of the structure was that there was no pillars inside to support it. Instead, Andrew applied the principles of tunnel construction by installing the outer steel frame to which concrete rings were attached via struts. This way, both the external frame and concrete rings carried the weight of the structure and decorative glass panels.
The construction looked very futuristic and spacious since there were no pillar inside to impede the free movements of passengers. It was innovative and impressive design. However it had to be built in perfect static balance to hold. The administrative investigation committee that invvestigated the accident cited 2 key facotrs leading to this. First was the structural engineering failure. The construction had design flaws. The design was on the edge of static balance. Terminal 2E lacked redundant supports, an otherwise standard construction feature added as a precaution measure in case one or more support fails.Terminal 2E had none and when the support failed, it shifted the load to other supports which ultimatly led to a collapse. The committeee also cited that the support failed in the first place because of their inadequate strenght and low resistance to temperature changes. On the day before the accident, temperatures varied from 20 to 4 degrees celsius. It was too much of a stress for the weak outer frame. The entire structure was labeled as having an inadequate capacity to resist stress. During 11 months of existence, the stress gradually weakened the structure u ntil it finally collapsed. Second factor was the process failure. The firm that built the terminal was the french company Aéroports de Paris. It was in charge of both designing and constructing the terminal, meaning there was no contrl on how the project was carried out. To cut the expenses and shorten the construction period, ADP cut some corners and circumvented essential protocols such as detailed analysis of the structure. The committee also noticed that the external support frame was chosen based on his aesthetic appeal rather than on calculating engineering judgement. Rather than consulting the construction engineers the management of the ADP increased pressure on them to finish the job earlier and at a lesser cost which led to mistakes in the construction process.
.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

12 Floors Gone in Two Seconds - The Surfside Condominium Disaster
An hour after midnight, a thundering noise awakens the entire Surfside neighborhood. Dozens of half-asleep occupants go out onto their terraces to see what is going on. It is as if an earthquake shakes the town. The noise comes from one particular place - the Champlain Towers South.
However, the condominium is replaced by a massive cloud of dust rising in the air. Once it settles down, it reveals a horrible truth. The Miami condo morphs into a huge pile of rubble, one of the worst construction disasters in American history. The disaster has been building for decades. A coupe of minutes because the collapsing, a couple was enjoying a night in the hotel next to Champlain tower south They noticed something strange at the garage entrance. There was a pile of concrete rubble on the floor. Water was pouring in streams from the ceiling. Champlain tower's condo had its own pool. It seemed like water was leaking to the garage. Aroudn 1 : 22 am, the concrete beams ont he garage ceiling broke and the pool deck caved in a loud noise, woke up residents. The entire deck collapsed on cars parcked in the garage. Second after, the disaster would strike them. After the pool deck caved in, the adjacent central broke off from the rest of the building and crashed down. From distance it looks like a collapse from a controlled explosion but it was in fact a disaster. It was what experts call a pancake collapse. The cutt off northeast corner of the building stood for a few more seconds before giving away. The entire event last for less than 12 seconds. Once dust settled, it revealed a hair rising situation.
The western portion of champlain tower south was still standing in its northern part, where it connected to the central section were the exposed remains of destroyed condos. It looked as if someone ripped off a piece of the building. In one of the apartments on the top floor, a children 's bunk bed stood just a few inches from the abyss. Beneath, a 3 story high pile of iron and concrete with people buried beneath it. 1 minute after the collapse, the local fire brigade receive the first emergency call. It was a war zone like situation. People were rushing from the still standing part of the building. From beneath the rubble, voices screamed for help. Some residents emerged from the ruins. Hundreds of firefighters and police officers arrived. By 4 am the rescue operation was in full swing. Special teams with search dogs were engaged while powerful air jacks were brought in to deal with the heavy concrete blocks. Jonah Handler and his mum Stacy Dawn were among the first rescued. Sadly the mum was trapped deeper, rescued later and passed away. 35 residents in total were rescued. However 159 residents were still missing. A reunification center for families was formed at the surfside community center. People were pouring in looking for lost friends and relatives. FEMA Urban search and rescue task force, teams of US Army corps enginners, even a foreign unit from israeli defense forces were also brought on the scene of the disaster. The opration alsted for days. Work on the ground was hindered by an undergroud fire that filled the cavities inside the wrecks with smoke. The number of missing gradually decreased over days but with no survivors among them. On 1st July 2021, after 1 week of efforts, there were 18 deads and 143 missing. But the operation had to be called off because the rescuer's safety was threatened by the westtern wing of the building. still standing and dangerously leaning toward their heads.
Experts believed it would collapse within days. To make things worse, forecast annouce that the tropical storm Elsa soon hit Florida, further destabilizaing the building's structure and debris. Rescuers needed to work fast. To locate more survivors, the rescuers brought in thermal cameras and drones yet the oods were grim. The death toll rose to 24 and the time was ticking away. The still standing portion of the building was to be demolished. A company specialized in taking down the buildings set the explosives in the foundation. However residents were reticent and 18 000 signatures were gathered to postpone it until all theit pets were found. On July 5th at 10 : 30 pm, the western portion was demolished. 20 minutes later, the recovery teams continued their operations. On July 6th, the Elsa stormed roared across Florida. Despite the weather conditions, the rescuers opened the entrance to some of the previously inaccessible areas of rubble. But it only allowed them to recover more dead bodies with the death roll reaching 36, increasing to 46 within 24 hours. At this point, 2 weeks after the disaster, it was evident that finding any survivor would be a true miracle. Therefore, the operation was shifted to search and recovery. The efforts lasted until July 26, 2021 when the last victim's body was found. At the end, the death toll reached 98. Only 3 residents survived the collapse. Champlain Tower South was far from low budget real estate. Condos in the building were listed as 600 000 to 700 000 dollars. The exclusive penthouse was sold a couple of months prior to the disaster for just under 3 million dollars. Building amenities included a 24 hours cerge surveillance. System valet, barbecue area, gym, sauna, hot tub, and a heated outdoor pool. It was hard to beleive that this building would have such structural problems.
In October 2018, the engineering firm morabito consultants was hired to inspect the building. One of the critical points in the report was the pool deck waterproofing problem. This and all the planter waterproofing was beyond its useful life and needed to be removed and replaced because it was causing major structural damage to the concrete structural slab below these areas. The report said that failing to replace this would cause in the future the extent of the concrete deterioration to expand exponentially. The inspection noted cracks and concrete colum beams and walls supporting the parking garage under the pool deck. However, even though the report underlined the necessity of repairing the waterproofing to ensure the safety of the residents, it did not indicate that the building was at risk of collapse. Morbido didn't submit the report to the city's authorities. The repair would cost 15 million dollars. A hefty price and a sensitive one considering the extent of the work required. The condo association agreed on the proposal and took the credit to finance the repairs. First step of the project was to fix the roof since its structure also had deteriorated. By the time of the collapse, contractors were still working on the boj. However it turned out there were more pressing repairs. 3 days before disaster, a pool contractor carried out a full inspection to make a bid for its restoration. When he saw beneath the pool deck shocked him inside the equipment room. There was water all over the floor, large cracks in the cracking walls and ceiling exposed, a rusty rebar. Since 1981 when the building was built, rebar inside the concrete structure holding the pool deck was gradually deteriorating. It was a process that lasted for teh full 40 years. Then the collapse of the pool deck slab undermined the base of the central section of the building.
A short time after, the central part of the building caved in toward the pool deck. An investigation committee from the national institute of standards and technology hsa yet to determine the cause of the collapse more than 1 year after the disaster. Experts examined what could have contributed to the demolition of the condominium, meanign it could last for years. The tower was close to beach so the commitee investigated the effects of salt, humidity and other environmental conditions. There was also doubt about the quality construction of the building. A forensic engineering experthired by the town of surfside to investigate collapse, Allyn E Kilsheimer said that rebars inside the concrete beams were not arranged in a way the original project called for. He expressed doubts about the rebars used to reinforce the structure. Given the building investors were accused of allegedly bribing the local officials to get the permit to constrthe condominium. But in 2021 the ones who designed, invested and made the building were already dead. Condo association company responsible for building and maintaining the building was blamed, just like the city of surfside. On June 23rd 2022, a day before the disaster's anniversary, Michael Hansman, Miami's C Circuit judge approved a 1,02 billion of dollar tentative settlement between the accused and the victim's families and owners of the demolished condominium.
An hour after midnight, a thundering noise awakens the entire Surfside neighborhood. Dozens of half-asleep occupants go out onto their terraces to see what is going on. It is as if an earthquake shakes the town. The noise comes from one particular place - the Champlain Towers South.
However, the condominium is replaced by a massive cloud of dust rising in the air. Once it settles down, it reveals a horrible truth. The Miami condo morphs into a huge pile of rubble, one of the worst construction disasters in American history. The disaster has been building for decades. A coupe of minutes because the collapsing, a couple was enjoying a night in the hotel next to Champlain tower south They noticed something strange at the garage entrance. There was a pile of concrete rubble on the floor. Water was pouring in streams from the ceiling. Champlain tower's condo had its own pool. It seemed like water was leaking to the garage. Aroudn 1 : 22 am, the concrete beams ont he garage ceiling broke and the pool deck caved in a loud noise, woke up residents. The entire deck collapsed on cars parcked in the garage. Second after, the disaster would strike them. After the pool deck caved in, the adjacent central broke off from the rest of the building and crashed down. From distance it looks like a collapse from a controlled explosion but it was in fact a disaster. It was what experts call a pancake collapse. The cutt off northeast corner of the building stood for a few more seconds before giving away. The entire event last for less than 12 seconds. Once dust settled, it revealed a hair rising situation.
The western portion of champlain tower south was still standing in its northern part, where it connected to the central section were the exposed remains of destroyed condos. It looked as if someone ripped off a piece of the building. In one of the apartments on the top floor, a children 's bunk bed stood just a few inches from the abyss. Beneath, a 3 story high pile of iron and concrete with people buried beneath it. 1 minute after the collapse, the local fire brigade receive the first emergency call. It was a war zone like situation. People were rushing from the still standing part of the building. From beneath the rubble, voices screamed for help. Some residents emerged from the ruins. Hundreds of firefighters and police officers arrived. By 4 am the rescue operation was in full swing. Special teams with search dogs were engaged while powerful air jacks were brought in to deal with the heavy concrete blocks. Jonah Handler and his mum Stacy Dawn were among the first rescued. Sadly the mum was trapped deeper, rescued later and passed away. 35 residents in total were rescued. However 159 residents were still missing. A reunification center for families was formed at the surfside community center. People were pouring in looking for lost friends and relatives. FEMA Urban search and rescue task force, teams of US Army corps enginners, even a foreign unit from israeli defense forces were also brought on the scene of the disaster. The opration alsted for days. Work on the ground was hindered by an undergroud fire that filled the cavities inside the wrecks with smoke. The number of missing gradually decreased over days but with no survivors among them. On 1st July 2021, after 1 week of efforts, there were 18 deads and 143 missing. But the operation had to be called off because the rescuer's safety was threatened by the westtern wing of the building. still standing and dangerously leaning toward their heads.
Experts believed it would collapse within days. To make things worse, forecast annouce that the tropical storm Elsa soon hit Florida, further destabilizaing the building's structure and debris. Rescuers needed to work fast. To locate more survivors, the rescuers brought in thermal cameras and drones yet the oods were grim. The death toll rose to 24 and the time was ticking away. The still standing portion of the building was to be demolished. A company specialized in taking down the buildings set the explosives in the foundation. However residents were reticent and 18 000 signatures were gathered to postpone it until all theit pets were found. On July 5th at 10 : 30 pm, the western portion was demolished. 20 minutes later, the recovery teams continued their operations. On July 6th, the Elsa stormed roared across Florida. Despite the weather conditions, the rescuers opened the entrance to some of the previously inaccessible areas of rubble. But it only allowed them to recover more dead bodies with the death roll reaching 36, increasing to 46 within 24 hours. At this point, 2 weeks after the disaster, it was evident that finding any survivor would be a true miracle. Therefore, the operation was shifted to search and recovery. The efforts lasted until July 26, 2021 when the last victim's body was found. At the end, the death toll reached 98. Only 3 residents survived the collapse. Champlain Tower South was far from low budget real estate. Condos in the building were listed as 600 000 to 700 000 dollars. The exclusive penthouse was sold a couple of months prior to the disaster for just under 3 million dollars. Building amenities included a 24 hours cerge surveillance. System valet, barbecue area, gym, sauna, hot tub, and a heated outdoor pool. It was hard to beleive that this building would have such structural problems.
In October 2018, the engineering firm morabito consultants was hired to inspect the building. One of the critical points in the report was the pool deck waterproofing problem. This and all the planter waterproofing was beyond its useful life and needed to be removed and replaced because it was causing major structural damage to the concrete structural slab below these areas. The report said that failing to replace this would cause in the future the extent of the concrete deterioration to expand exponentially. The inspection noted cracks and concrete colum beams and walls supporting the parking garage under the pool deck. However, even though the report underlined the necessity of repairing the waterproofing to ensure the safety of the residents, it did not indicate that the building was at risk of collapse. Morbido didn't submit the report to the city's authorities. The repair would cost 15 million dollars. A hefty price and a sensitive one considering the extent of the work required. The condo association agreed on the proposal and took the credit to finance the repairs. First step of the project was to fix the roof since its structure also had deteriorated. By the time of the collapse, contractors were still working on the boj. However it turned out there were more pressing repairs. 3 days before disaster, a pool contractor carried out a full inspection to make a bid for its restoration. When he saw beneath the pool deck shocked him inside the equipment room. There was water all over the floor, large cracks in the cracking walls and ceiling exposed, a rusty rebar. Since 1981 when the building was built, rebar inside the concrete structure holding the pool deck was gradually deteriorating. It was a process that lasted for teh full 40 years. Then the collapse of the pool deck slab undermined the base of the central section of the building.
A short time after, the central part of the building caved in toward the pool deck. An investigation committee from the national institute of standards and technology hsa yet to determine the cause of the collapse more than 1 year after the disaster. Experts examined what could have contributed to the demolition of the condominium, meanign it could last for years. The tower was close to beach so the commitee investigated the effects of salt, humidity and other environmental conditions. There was also doubt about the quality construction of the building. A forensic engineering experthired by the town of surfside to investigate collapse, Allyn E Kilsheimer said that rebars inside the concrete beams were not arranged in a way the original project called for. He expressed doubts about the rebars used to reinforce the structure. Given the building investors were accused of allegedly bribing the local officials to get the permit to constrthe condominium. But in 2021 the ones who designed, invested and made the building were already dead. Condo association company responsible for building and maintaining the building was blamed, just like the city of surfside. On June 23rd 2022, a day before the disaster's anniversary, Michael Hansman, Miami's C Circuit judge approved a 1,02 billion of dollar tentative settlement between the accused and the victim's families and owners of the demolished condominium.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

Field Trip Of Horror (Cave Creek Disaster)
The in-depth story of the Cave Creek Platform Collapse Disaster 1995. A viewing platform hangs 130 feet over one of New Zealand's natural wonders, offering unparalleled canyon views. But for a group of young, enthusiastic students, it’s the last thing they ever see. Cave creek is a natural marvel on New Zealand's west coast. A limestone cave formed by acid water. Here the visitors can see the resurgence where streams emerge from an underground cave system. It's a geological phenomenon that lures hundreds yearly. In 1993 the park made an overhanging viewing plateform. nearby. Fast forward a few years, and a group of students with their tutor from an outdoor recreation were looking forward to visit the cave creek, making the platform the highlight of their excursion. Shirley Slatter, conservation officer accompanying the students, noticed an unusual flexing of the cave creek viewing platform when another group stood on it. He reported it to the newly appointed field center manager Steven O Dea. They split in 2 groups and the alrger group reached the platform first with 17 students to look at the headwaters coming out of the cave system, the students even joking about the platforme structure. In less than 1 minute, the platform suddently broke away from its support and fell into the ground, crashing down nearly 100 feets below the trees, slamming into the chasms floor amongst the large jagged rocks. Moments later, the second group consisting of the tutor, field officer and 3 students reached the viewing deck and saw the scene. The conservation officer and another student reached the group's vehicles for help but keys were missing. Another student races 5 miles to alert the Greymouth police. 1 hour after the tragedy, the call for emergency assistance was made and helicopters, ambulances and teams were raced to the sceneIn the fall, 14 lives were lost, 13 students and conservation officer OD. Of the 18 people on the platform, 12 deid instantly from the fall.
The remaining 6 survived the initial fall but by the time the emergency responders arrived, 2 more died from their injuries. The platform project was poised to be a tragedy from the beginning. According to the doc report, no professional enginners or architects were involved in the design of the proposed platform. Well intentionned by no qualified officer drew the plans. A 10 x 10 feets decking with an overhang of approximately 5 feet would be canal levered and once the project got its funding in June 1992. The deck was built outside and and was delivered by helicopter to the site while other material . It was supposed to be suspended over the sharp drop. Problem is that it was built by DOC staff members, not by qualified builders or engineers. Only one of the crew previously worked with Timber. The plans for installation were not even used on the site to make matters worse. This means the posts were hammered into the groudn wherever the rough sound would allow. As a result, the load on the platform wasn't spread out equally. The person who made the plans was on the site that day but their job was to clear the trail leading to the platform. Plus, the bolts supposed to hold the platform in place were brought to the site without a drill. No nails were used. Instead, after a rigorous day of constructionthe 4 men who built the platform got into it to take a picture. The lack of structural integrity was shocking. Less than 1 year after the construction, in april 1994, the platform steps were poured finally. But they were not properly secured. On top of that there were no instructions on how to use the steel to connect the concrete steps to the platform and make the support that a suspended structure needs. When the platform structure was shown to local conservation board a few months later, a chairman asked if it had proper permits. It prompted staff to get approval retroactively. Those attempts were never successfully carried out.
The platform was not listed in any register that would have resulted in regular inspections.
A warning sign for the platform, suggesting a maximum limit of five people, had been ordered but was never installed at the site.
7 minutes.
The Subway Disaster That Changed Firefighting
The in-depth story of the King's Cross Station Fire 1987 - The Subway Disaster That Changed Firefighting.
The London Fire brigade receives a call to respond to one of London’s underground stations. The King’s Cross is on fire. Four engines are dispatched to the scene and arrive within minutes.
The blaze is at an escalator leading down to one of the station platforms. It’s only a small fire though, nothing a hose spray can’t handle. At least, that’s what they think.
Instead of a small fire, the London Tube is struck by the worst blaze in its history.
The in-depth story of the Cave Creek Platform Collapse Disaster 1995. A viewing platform hangs 130 feet over one of New Zealand's natural wonders, offering unparalleled canyon views. But for a group of young, enthusiastic students, it’s the last thing they ever see. Cave creek is a natural marvel on New Zealand's west coast. A limestone cave formed by acid water. Here the visitors can see the resurgence where streams emerge from an underground cave system. It's a geological phenomenon that lures hundreds yearly. In 1993 the park made an overhanging viewing plateform. nearby. Fast forward a few years, and a group of students with their tutor from an outdoor recreation were looking forward to visit the cave creek, making the platform the highlight of their excursion. Shirley Slatter, conservation officer accompanying the students, noticed an unusual flexing of the cave creek viewing platform when another group stood on it. He reported it to the newly appointed field center manager Steven O Dea. They split in 2 groups and the alrger group reached the platform first with 17 students to look at the headwaters coming out of the cave system, the students even joking about the platforme structure. In less than 1 minute, the platform suddently broke away from its support and fell into the ground, crashing down nearly 100 feets below the trees, slamming into the chasms floor amongst the large jagged rocks. Moments later, the second group consisting of the tutor, field officer and 3 students reached the viewing deck and saw the scene. The conservation officer and another student reached the group's vehicles for help but keys were missing. Another student races 5 miles to alert the Greymouth police. 1 hour after the tragedy, the call for emergency assistance was made and helicopters, ambulances and teams were raced to the sceneIn the fall, 14 lives were lost, 13 students and conservation officer OD. Of the 18 people on the platform, 12 deid instantly from the fall.
The remaining 6 survived the initial fall but by the time the emergency responders arrived, 2 more died from their injuries. The platform project was poised to be a tragedy from the beginning. According to the doc report, no professional enginners or architects were involved in the design of the proposed platform. Well intentionned by no qualified officer drew the plans. A 10 x 10 feets decking with an overhang of approximately 5 feet would be canal levered and once the project got its funding in June 1992. The deck was built outside and and was delivered by helicopter to the site while other material . It was supposed to be suspended over the sharp drop. Problem is that it was built by DOC staff members, not by qualified builders or engineers. Only one of the crew previously worked with Timber. The plans for installation were not even used on the site to make matters worse. This means the posts were hammered into the groudn wherever the rough sound would allow. As a result, the load on the platform wasn't spread out equally. The person who made the plans was on the site that day but their job was to clear the trail leading to the platform. Plus, the bolts supposed to hold the platform in place were brought to the site without a drill. No nails were used. Instead, after a rigorous day of constructionthe 4 men who built the platform got into it to take a picture. The lack of structural integrity was shocking. Less than 1 year after the construction, in april 1994, the platform steps were poured finally. But they were not properly secured. On top of that there were no instructions on how to use the steel to connect the concrete steps to the platform and make the support that a suspended structure needs. When the platform structure was shown to local conservation board a few months later, a chairman asked if it had proper permits. It prompted staff to get approval retroactively. Those attempts were never successfully carried out.
The platform was not listed in any register that would have resulted in regular inspections.
A warning sign for the platform, suggesting a maximum limit of five people, had been ordered but was never installed at the site.
7 minutes.
The in-depth story of the King's Cross Station Fire 1987 - The Subway Disaster That Changed Firefighting.
The London Fire brigade receives a call to respond to one of London’s underground stations. The King’s Cross is on fire. Four engines are dispatched to the scene and arrive within minutes.
The blaze is at an escalator leading down to one of the station platforms. It’s only a small fire though, nothing a hose spray can’t handle. At least, that’s what they think.
Instead of a small fire, the London Tube is struck by the worst blaze in its history.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

The Lake Peigneur Giant Sinkhole Disaster 1980
The in-depth story of the Lake Peigneur Drilling Accident: When The Earth Swallowed a Lake.
November 20, 1980, is a new day at Lake Peigneur in Louisiana. Some 9 miles north of the Vermilion Bay in the Gulf of Mexico, a charming, calm lake is a popular resort for fishermen and nature lovers.. However not everyone is interested by the lake's natural beauty. Oil drilling platform in ownership of Wilson brothers corporation brought to the lake. Hired by the famous texano oil company, Wilson Brothers were looking for oil Beneath the lake lies a gigantic salt dome meaning oil was probably near. Wilson Brothers were suppoed to drill down to it. Their employees have done the job many times before and are experienced. Once the enginners gave the coordinates, they threw themselves into the job. Drilling for oil is a challenging job with unpredictable consequences such as accidents, like this one. Early in morning around 6 am, the 36 cm drill gets stuck at a depth of about 1 230 feet. Nothing too unusual for these workers who need to get the drill loose and keep working. However it seems that the drill won't come out no matter what they try. Suddently the drill tilts forcefully followed by a couple of loud pops.Undoubtly a situation that calls for an immediate evacuation of workers. In a hurry they cut free the barges holding the platform and flee to the safest part of the lake. They were right to evaccuate as the platform overturned and sank. Lake is just 10 feet deep and this massive oil drilling construction being swallowed surprised everyone. THe workers notice their boat is being pulled to the platform's location. The skipper pushes the throttle and takes the boat and the workers to safety of the lakeshore. The sunken platform turns out to be an event of catastrophic proportions with giant whirpool forming at the spot where the platform used to be, sucking in nearby barges and boats, soil from Jefferson island, trucks, trees, buildings.
Even a parking lot near the botanical garden are sucked into the giant vortex. The delcambre canal taking water from Lake Peigneur to the Gulf of Mexico reverses his flow under the influence of the whirpool. People aroud the lake are stunned. It seemed like the bowels of earth opened. The ground opened and all the water of the lake went into in. Below the lake there was a colossal salt dome, a vertical mass of salt that intrudes into upper layers of earth from underlying salt beds due to the weight of overlying rock. In the USA, salt domes are frequent especially along the Gulf of Mexico coastline. Most of them in Texas and Louisiana, all of them exploited for salt mining. Inside the salt dome beneath Lake Peigneur was 4 level salt mine reaching its depth of 1 500 feet, 157 meters. Under the ownership of Diamond Crystal Salt Company, the mine was opened in 1919 and was extracting halite minerals, better known as rock salt for 6 decades incessantly. The initial mining was conducted on the topmost level at a depth of 800 feet. Over time the primary salt production moved deeper with 3 new levels opened at the depth of 1 000, 1 300 and 1 500 feet. Each level consisted of large tunnels up to 100 feet high and wide. Tunnel on the bottommost level was 100 feet wide and 80 feet tall. Each of these tunnels was created through the process of mining. Inside them, vast pillars of salt were left untouched to support the tunnel ceiling. Like oil drilling, mining has its own risks. A record of mining related accidents is long and includes a whole palette of dangers, from ceiling collapses to outbursts of explosives gasses trapped in underground pockets. In salt mines, miners pay special attention to the stability of their tunnel because the entire structure lies on pillars made of teh same material they are digging out. The presence of water is hasardous, which could dissolve salt pillars and leave the tunnel ceiling without support.
The Jefferson island mine at Pake Peigneur had a couple of water leak incidesnts in the mid 1970 but none threatened the stability. The bigger problem was the stability of the entire mine above the 1 300 feet level. Due to the change of dimensions of narrow pillars on the upper floor due to prolonged stress, the surface was subsiding 10 inches per year. On the day of the accident, 55 miners descended to the bottom 2 level at 1 300 feet and 1 500 feet below ground. The shift began as usual. Using the electric shovel, they miend the rock salt, then transported it to the surface in small mining carts. However the job was disrupted by unusual sounds coming down the tunnel. The electrican Junius Gaddison found was coming from fuel drums banging against each other as they were carried down the tunnel by a knee deep stream of muddy water. He knew about a story of water leakage in the mine but a torrent of water was a clear signal that something was wrong. Miraculously, all 55 miners reached safety despite of a slow elevator that could only carry 8 persons a time. The drill got stuck because it penetrated the mine ceiling at 1 300 feet level, creating a funnel that allowed the water from the lake to leak into the mine. The water dissolved the rock salt around the drill as if it flowned down, creating a larger and larger funnel. Once amounts of water reached the mine, they began dissolving the salt pillars and cause the entire mine construction and everything above to collapse. In 3 hours the giant hole in the ground took all 3,5 billion gallons of water ( more than 13 billion liters ). The force of the whirpool was so strong that it drew water from the Delcambre canal. Because the water flowned into the mine faster than the air could get out, the air was compressed and burst out of the mine's air shaft and the water from Gulf of Mexico began filling the hole through the Delcambre canal, creating a temporary 150 feet waterfall.
.
The in-depth story of the Lake Peigneur Drilling Accident: When The Earth Swallowed a Lake.
November 20, 1980, is a new day at Lake Peigneur in Louisiana. Some 9 miles north of the Vermilion Bay in the Gulf of Mexico, a charming, calm lake is a popular resort for fishermen and nature lovers.. However not everyone is interested by the lake's natural beauty. Oil drilling platform in ownership of Wilson brothers corporation brought to the lake. Hired by the famous texano oil company, Wilson Brothers were looking for oil Beneath the lake lies a gigantic salt dome meaning oil was probably near. Wilson Brothers were suppoed to drill down to it. Their employees have done the job many times before and are experienced. Once the enginners gave the coordinates, they threw themselves into the job. Drilling for oil is a challenging job with unpredictable consequences such as accidents, like this one. Early in morning around 6 am, the 36 cm drill gets stuck at a depth of about 1 230 feet. Nothing too unusual for these workers who need to get the drill loose and keep working. However it seems that the drill won't come out no matter what they try. Suddently the drill tilts forcefully followed by a couple of loud pops.Undoubtly a situation that calls for an immediate evacuation of workers. In a hurry they cut free the barges holding the platform and flee to the safest part of the lake. They were right to evaccuate as the platform overturned and sank. Lake is just 10 feet deep and this massive oil drilling construction being swallowed surprised everyone. THe workers notice their boat is being pulled to the platform's location. The skipper pushes the throttle and takes the boat and the workers to safety of the lakeshore. The sunken platform turns out to be an event of catastrophic proportions with giant whirpool forming at the spot where the platform used to be, sucking in nearby barges and boats, soil from Jefferson island, trucks, trees, buildings.
Even a parking lot near the botanical garden are sucked into the giant vortex. The delcambre canal taking water from Lake Peigneur to the Gulf of Mexico reverses his flow under the influence of the whirpool. People aroud the lake are stunned. It seemed like the bowels of earth opened. The ground opened and all the water of the lake went into in. Below the lake there was a colossal salt dome, a vertical mass of salt that intrudes into upper layers of earth from underlying salt beds due to the weight of overlying rock. In the USA, salt domes are frequent especially along the Gulf of Mexico coastline. Most of them in Texas and Louisiana, all of them exploited for salt mining. Inside the salt dome beneath Lake Peigneur was 4 level salt mine reaching its depth of 1 500 feet, 157 meters. Under the ownership of Diamond Crystal Salt Company, the mine was opened in 1919 and was extracting halite minerals, better known as rock salt for 6 decades incessantly. The initial mining was conducted on the topmost level at a depth of 800 feet. Over time the primary salt production moved deeper with 3 new levels opened at the depth of 1 000, 1 300 and 1 500 feet. Each level consisted of large tunnels up to 100 feet high and wide. Tunnel on the bottommost level was 100 feet wide and 80 feet tall. Each of these tunnels was created through the process of mining. Inside them, vast pillars of salt were left untouched to support the tunnel ceiling. Like oil drilling, mining has its own risks. A record of mining related accidents is long and includes a whole palette of dangers, from ceiling collapses to outbursts of explosives gasses trapped in underground pockets. In salt mines, miners pay special attention to the stability of their tunnel because the entire structure lies on pillars made of teh same material they are digging out. The presence of water is hasardous, which could dissolve salt pillars and leave the tunnel ceiling without support.
The Jefferson island mine at Pake Peigneur had a couple of water leak incidesnts in the mid 1970 but none threatened the stability. The bigger problem was the stability of the entire mine above the 1 300 feet level. Due to the change of dimensions of narrow pillars on the upper floor due to prolonged stress, the surface was subsiding 10 inches per year. On the day of the accident, 55 miners descended to the bottom 2 level at 1 300 feet and 1 500 feet below ground. The shift began as usual. Using the electric shovel, they miend the rock salt, then transported it to the surface in small mining carts. However the job was disrupted by unusual sounds coming down the tunnel. The electrican Junius Gaddison found was coming from fuel drums banging against each other as they were carried down the tunnel by a knee deep stream of muddy water. He knew about a story of water leakage in the mine but a torrent of water was a clear signal that something was wrong. Miraculously, all 55 miners reached safety despite of a slow elevator that could only carry 8 persons a time. The drill got stuck because it penetrated the mine ceiling at 1 300 feet level, creating a funnel that allowed the water from the lake to leak into the mine. The water dissolved the rock salt around the drill as if it flowned down, creating a larger and larger funnel. Once amounts of water reached the mine, they began dissolving the salt pillars and cause the entire mine construction and everything above to collapse. In 3 hours the giant hole in the ground took all 3,5 billion gallons of water ( more than 13 billion liters ). The force of the whirpool was so strong that it drew water from the Delcambre canal. Because the water flowned into the mine faster than the air could get out, the air was compressed and burst out of the mine's air shaft and the water from Gulf of Mexico began filling the hole through the Delcambre canal, creating a temporary 150 feet waterfall.
.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

Florida's Most Horrific Industrial Accident
The in-depth story of the Tampa Electric Molten Slag Accident: “Mom, help me. I’m burning." These were the final words of a desperate son, trapped as molten slag poured around him. Although the explosion at Tampa Electric’s Big Bend Power Station was sudden, it wasn’t a random accident. Power demand was at his peak in Florida. There are coil boilers and 2 unit working at full capacity but it has become clogged with as making situation more precarious. So a senior plant manager rounds up 5 other employees to perform the maintainance. Among them, 21 years old Antonio Navarrete. He is newly in love and about to become a father. He lives with his parents and is determined to work hard to provide for his family. He has been on the job for only 4 days. He is about to perform one of the most hazardous task in the power. IN front of him stands a massive structure, unit 3, with a humongous 12 story boiler that burns coal to generate electricity. Unlike newer plants, Big Ben's boiler melt ash into molten slag, essentially lava heated to over 1 000 degrees. The slag collects at the bottom of the boiler and dumpts into a water filled tanks where it hardents into glassy rocks but today the slag just built up and clogged the mansiz hole that it's supposed to drop through and so the slag keeps building up on top of itself in the boiler down in the cooling tank. There is a separate problem : harden slag is blocking the grinder supposed to break it into small chips for industrial use. To keep energy production stable, the staff needed to fix these 2 issues quickly. Safe way would be to turn off unit 2's boiler and fix the blockages but shutting down isn't quick or easy. It's like stopping a freight train. Cooling the boiler and restarting would take hours, cost hundreds of thousands and risk power outages. Instead, the decision is made to clear the boulder in the tank while keeping the boiler running, counting on the slag bag above to remain clogged.
Experienced employees voiced their fears. So the company hired contractors for this risky task. Antonio was one of these contractors. Knowing the risks, a shift operator searches for the slag tank watre blasting procedure manual but it can't be found. Without it, no briefing safety is held before the work begins. First they drain the cooling water that usually cools the slag and reveal the blockage on top of the grinder. Then they open the doghouse door, the door closest to the ground. Antonio watches the other 5 men take turn, firing their high press water blasters through the door at the rocks. Above in the boiler, molten slag pool. It's like standing under a dam with a growing crack. The redhot slag pressing against it with relentless force then about 20 minutes into the operation, withotu warning, the blockage at the slag trap breaks loose, releasing thousands of gallons of superheated slag from the boiler. The lava gushes out of the tank through the doghosue door and covers the workers. The sheer volume and speed of the molten material are impossible to contain. The slag flows like a river of fire, covering the ground in a pool 6 feet deep and 40 feet wide. The intense heat vaporizes all the moisture in the air, creating a scalding steam cloud. that intensifies the situation. Some workers are trapped in the cauldron of fire. The advancing molten steam cuts off escape routes transforming the area into a deadly furnace. In this moment, Antonio manages to reach his phone, dials his mother's number but she doesn't pick up so he leaves a voicemail that will haunt her forever. The eruptionw as swift and merciless. When the 011 call is placed, it's clear that the control room has no idea of the full extent of the situation.
Emergency responders arrive within minutes but the scene is catastrophic. Senior plant operator Michael McCort and contractor Christopher Irvin are pronounced dead on site. The other 4, including Antonio are severely injured and the prognosis is grim. Burns from molten slags are some of the most devastating injuries, causing irreversible damages to the skin tissues and organs. Doctors could only place the survivors in medically induced comas. Even if medican teams had been on sight it's unlikely they could have saved the workers. The most obvious solution was to shut the boiler down. Beyond the cost and the time, Tampa Electric struggled to meet the electricity demand especially with temperature soaring and July 4th holyday approaching. Even more people were at home cranking up their ACS. If they shut down unit 2 they would have to buy power from other utilities at a much higher cost. To avoid outages and meet demands they made the dangerous choice to try to fix the clog at unit 2 without turning it off. Another reason was the decision to outsource these dangerous jobs rather after its workers and union members raised safety concerns, particularly about performing maintainance while the boiler was still running. By bringing in contractors, TECO could continue these high risk tasks but the contractors may not be as familiar with the plant's aging equipment which only increased the dangers. Although OSHA regulations give workers the right to refuse a job if they believe their life is in danger. Despite raising concerns about the risks of working on the slag tanks while the boiler was still operationnal. The job proceeded with contractors instead. This move also created safety gaps because contractors weren't as closely involved in TECO's regular safety practices. Despite what the CEO claime ( Gordon Gillette ).
The company's later admission made us know that it was not an isolated accident. 20 years before, more workers died at Tampa Electric's power plants than at those who run by any other Florida utility. TECO registered 1O work related deaths while no other utility had more than 3 fatalities. An accident that happened 20 years before June 29th, 2017. In June 1997, 4 employees were seriously injured when hot slags spewed from a tank during a familiar maintainance operation, causing first and second degrees burns. After this, TECO implemented a strict policy against performing maintenance on slag tankswhile the boiler was operationnal. Somehow over the years the policy simply eroded. By 2015, union members started raising concerns that they were asked to work on slag tanks with the boilers running. Federal investigator found Tampa Electric ignored its own rule and initially found the utility close to 130 000 dollars. However as investigations were ungoing, TECO was charged with violating works safety guidelines. 5 years after the accident, Tampa Electric admitted skipping mandatory safety training, a simple task that could have saved lives. As a result, the company was fined 500 000 dollars and given 3 years of probation for knowingly violating the rule. The the family's victims, it was a mere slam on the wrist. TECO eventually reached confidential settlements with them, no compensation could ever undo the loss. Despite the efforts of the medical staff, Antonio Navarrete, Armando Petes and Frank Jones all died in the days and weeks following the accident. The only survivor was Gary Marine Junior. Antonio's child will grow without knowing his father all because of the decisions made that day.
The in-depth story of the Tampa Electric Molten Slag Accident: “Mom, help me. I’m burning." These were the final words of a desperate son, trapped as molten slag poured around him. Although the explosion at Tampa Electric’s Big Bend Power Station was sudden, it wasn’t a random accident. Power demand was at his peak in Florida. There are coil boilers and 2 unit working at full capacity but it has become clogged with as making situation more precarious. So a senior plant manager rounds up 5 other employees to perform the maintainance. Among them, 21 years old Antonio Navarrete. He is newly in love and about to become a father. He lives with his parents and is determined to work hard to provide for his family. He has been on the job for only 4 days. He is about to perform one of the most hazardous task in the power. IN front of him stands a massive structure, unit 3, with a humongous 12 story boiler that burns coal to generate electricity. Unlike newer plants, Big Ben's boiler melt ash into molten slag, essentially lava heated to over 1 000 degrees. The slag collects at the bottom of the boiler and dumpts into a water filled tanks where it hardents into glassy rocks but today the slag just built up and clogged the mansiz hole that it's supposed to drop through and so the slag keeps building up on top of itself in the boiler down in the cooling tank. There is a separate problem : harden slag is blocking the grinder supposed to break it into small chips for industrial use. To keep energy production stable, the staff needed to fix these 2 issues quickly. Safe way would be to turn off unit 2's boiler and fix the blockages but shutting down isn't quick or easy. It's like stopping a freight train. Cooling the boiler and restarting would take hours, cost hundreds of thousands and risk power outages. Instead, the decision is made to clear the boulder in the tank while keeping the boiler running, counting on the slag bag above to remain clogged.
Experienced employees voiced their fears. So the company hired contractors for this risky task. Antonio was one of these contractors. Knowing the risks, a shift operator searches for the slag tank watre blasting procedure manual but it can't be found. Without it, no briefing safety is held before the work begins. First they drain the cooling water that usually cools the slag and reveal the blockage on top of the grinder. Then they open the doghouse door, the door closest to the ground. Antonio watches the other 5 men take turn, firing their high press water blasters through the door at the rocks. Above in the boiler, molten slag pool. It's like standing under a dam with a growing crack. The redhot slag pressing against it with relentless force then about 20 minutes into the operation, withotu warning, the blockage at the slag trap breaks loose, releasing thousands of gallons of superheated slag from the boiler. The lava gushes out of the tank through the doghosue door and covers the workers. The sheer volume and speed of the molten material are impossible to contain. The slag flows like a river of fire, covering the ground in a pool 6 feet deep and 40 feet wide. The intense heat vaporizes all the moisture in the air, creating a scalding steam cloud. that intensifies the situation. Some workers are trapped in the cauldron of fire. The advancing molten steam cuts off escape routes transforming the area into a deadly furnace. In this moment, Antonio manages to reach his phone, dials his mother's number but she doesn't pick up so he leaves a voicemail that will haunt her forever. The eruptionw as swift and merciless. When the 011 call is placed, it's clear that the control room has no idea of the full extent of the situation.
Emergency responders arrive within minutes but the scene is catastrophic. Senior plant operator Michael McCort and contractor Christopher Irvin are pronounced dead on site. The other 4, including Antonio are severely injured and the prognosis is grim. Burns from molten slags are some of the most devastating injuries, causing irreversible damages to the skin tissues and organs. Doctors could only place the survivors in medically induced comas. Even if medican teams had been on sight it's unlikely they could have saved the workers. The most obvious solution was to shut the boiler down. Beyond the cost and the time, Tampa Electric struggled to meet the electricity demand especially with temperature soaring and July 4th holyday approaching. Even more people were at home cranking up their ACS. If they shut down unit 2 they would have to buy power from other utilities at a much higher cost. To avoid outages and meet demands they made the dangerous choice to try to fix the clog at unit 2 without turning it off. Another reason was the decision to outsource these dangerous jobs rather after its workers and union members raised safety concerns, particularly about performing maintainance while the boiler was still running. By bringing in contractors, TECO could continue these high risk tasks but the contractors may not be as familiar with the plant's aging equipment which only increased the dangers. Although OSHA regulations give workers the right to refuse a job if they believe their life is in danger. Despite raising concerns about the risks of working on the slag tanks while the boiler was still operationnal. The job proceeded with contractors instead. This move also created safety gaps because contractors weren't as closely involved in TECO's regular safety practices. Despite what the CEO claime ( Gordon Gillette ).
The company's later admission made us know that it was not an isolated accident. 20 years before, more workers died at Tampa Electric's power plants than at those who run by any other Florida utility. TECO registered 1O work related deaths while no other utility had more than 3 fatalities. An accident that happened 20 years before June 29th, 2017. In June 1997, 4 employees were seriously injured when hot slags spewed from a tank during a familiar maintainance operation, causing first and second degrees burns. After this, TECO implemented a strict policy against performing maintenance on slag tankswhile the boiler was operationnal. Somehow over the years the policy simply eroded. By 2015, union members started raising concerns that they were asked to work on slag tanks with the boilers running. Federal investigator found Tampa Electric ignored its own rule and initially found the utility close to 130 000 dollars. However as investigations were ungoing, TECO was charged with violating works safety guidelines. 5 years after the accident, Tampa Electric admitted skipping mandatory safety training, a simple task that could have saved lives. As a result, the company was fined 500 000 dollars and given 3 years of probation for knowingly violating the rule. The the family's victims, it was a mere slam on the wrist. TECO eventually reached confidential settlements with them, no compensation could ever undo the loss. Despite the efforts of the medical staff, Antonio Navarrete, Armando Petes and Frank Jones all died in the days and weeks following the accident. The only survivor was Gary Marine Junior. Antonio's child will grow without knowing his father all because of the decisions made that day.
il y a 8 mois
Post.

7 Worst Disasters That Were EASY to Prevent
Part 2
Then there is the parade stampede disaster in Germany. A catastrophic crush that left the nation in shock. It was one of the largest festivals in Europe and a landmark of German culture. In 2010, Duisberg hosts the parade. Music trucks drive around the festival. Some of Europe's top DJ are set to perform. But with each minute, the crowd grows larger and larger, causing the festive spirit to fade away. On the main ramp, thousands of visitors packed. People start to scream and call for help. It turns into a horror scene taking 21 young lives. The love parade caused controversy throughout its history, starting in 1989 as a parade of 150 people onf the streets of west Berlin. 8 years later it became on of the largest parties in the world with 1 million festival goers dancing on the STS and Yuni int he center of the German capital. Despite oppositions, there were still many people attending and some were concerned by issues liked the environmental damage, illegal drug trafficking and safety regulations. Because of the latter the senate of Berlin denied a permit to the event organizers. In 2007 the love parade moved to the Ruhr area. First host city was Essen followed by Dortmund. In 2009 the Bochum love parade was cancelled and finally in 2010 Duisburg hosted the event. Essen and Dortmund events were successful with respectively 1,2 million and 1,6 million visitors. So Duisburg wanted to be as successful. The european capital of the culture campaign was a reason to host the event. The city's mayor, Adolf Sauerland was determined to make the love parade the best ever, especially because of the forecast of 1,4 million visitors. The city's authorities decided to organize the event at all causes. First there was concern that the event site was not appropriate for so many people.
The city and the parade organizer agreed to set the parade at the former freight station with a total area of 120 000 square yars, too small to take 1,4 million visitors. To adress the issue a compromise was made to limit the amount of people to 250 000. In addition, the area was fenced to meet the requirements of German safety regulations. The entry of the old freight station was more concerning than the small area for the parade. The opening LED towards the main entrance across the so called ramp. The ramp was supposed to take all the visitors arriving at the parade. Problem was that the same route including a narrower side ramp west of the main ramp also served as the exit route from the main event V area. It was not the time for Lent Gamba and its owner Riner Scher to organize the parade. They hired a crowd researched to clear the doubts about the safety issues. He made a study about a detailed evacuation in case of danger. Calculation of inflow and outflow if visitors showed that the main ramp was suitable as an entry point, bordered by high walls. It was 85 feet wide and 426 feet long. Its maximum flow would be approximately 115 000 visitors per hour. The most traffic was expected between 1 700 hours and 1 800 hours with almost 1 million of people arriving in the area and 55 000 people leaving. Despite plans and studies, it ended as a disaster. Things complicated even before the event as the festival gates were opened at 11 : 00 am. But due to prolonged contsuctions in central areas, the opening was delayed by 1 hour. When tha gates opened, a large group of people was already waiting and thousands of partygoers lined up from both sides of the tunnel in 1 hour.
The main idea was to drawn the visitors to join the parade and to continue walking along the route. In reality, they obstructed those entering the main area thus slowing down the inflow. The jam at the float's path caused the concentration of people at the main ramp to increase. The entire ramp up to the tunnel was crowded at 14 : 42. Unable to keep the flow of people in and out of the main area, the organizers tried to have support from police. Pushers were engaged those roles was to help people go forward and release the pressure at the main ramp. No one was allowed to leave the site either. What the police believed was a solution only aggravated the situation. The crowd the cordon and the entrance gate didn't reduce. Visitors trying to enter the festival area collided with those wanting to leave. People arriving at the parade was so large that inevitably the cordons would break. The first collapsed at the eastern end followed by the one at the western end. At 16 : 21 a torrent of people rushed towards the main ramp where the third cordon was still holding. As a result no one could move in or out of the area on either side of the police's third cordon. .Some people began climbing poles and traffic signs and other structures to reach the main site above them. Under the crowd's pressure, police dissolved the third cordon, leaving those on the main ramp on their own. Then some of the visitors found a way out via a narrow staircase at the western wall above the tunnel opening.
In a flash, crowd turbulence arose with everyone wanting to climb up. Police tried to control the commotion around them. People kept pouring from the west end of the tunnel making the crowding near the narrow staircases unbearable. When the police removed the fence in the tunnel to let the ambulance pass, hundreds of attendees use the opportunity to rush toward the ramp. Even with the police announcing that the festival area was full and not accessible, it didn't change. Dozens of bodies fell unconscious. Many struggled to stay on their feets. Rainer Schaller, organizer of the parade, meanwhile did an interview describing the parade as a complete success, not aware about the people dying only a couple of yards away. Emergency vehicles began to arrive at the scenes as dozens of people lay on the floor with no sign of life. Police tried to organize and limit the number of people trying to climb the stairs. The density at the ramp reduced but the situation was still critical. Desperate cries for help rang out. Situation cleared up only at 17 : 16 while first fatalities were already reported at 17 : 02.
Part 2
Then there is the parade stampede disaster in Germany. A catastrophic crush that left the nation in shock. It was one of the largest festivals in Europe and a landmark of German culture. In 2010, Duisberg hosts the parade. Music trucks drive around the festival. Some of Europe's top DJ are set to perform. But with each minute, the crowd grows larger and larger, causing the festive spirit to fade away. On the main ramp, thousands of visitors packed. People start to scream and call for help. It turns into a horror scene taking 21 young lives. The love parade caused controversy throughout its history, starting in 1989 as a parade of 150 people onf the streets of west Berlin. 8 years later it became on of the largest parties in the world with 1 million festival goers dancing on the STS and Yuni int he center of the German capital. Despite oppositions, there were still many people attending and some were concerned by issues liked the environmental damage, illegal drug trafficking and safety regulations. Because of the latter the senate of Berlin denied a permit to the event organizers. In 2007 the love parade moved to the Ruhr area. First host city was Essen followed by Dortmund. In 2009 the Bochum love parade was cancelled and finally in 2010 Duisburg hosted the event. Essen and Dortmund events were successful with respectively 1,2 million and 1,6 million visitors. So Duisburg wanted to be as successful. The european capital of the culture campaign was a reason to host the event. The city's mayor, Adolf Sauerland was determined to make the love parade the best ever, especially because of the forecast of 1,4 million visitors. The city's authorities decided to organize the event at all causes. First there was concern that the event site was not appropriate for so many people.
The city and the parade organizer agreed to set the parade at the former freight station with a total area of 120 000 square yars, too small to take 1,4 million visitors. To adress the issue a compromise was made to limit the amount of people to 250 000. In addition, the area was fenced to meet the requirements of German safety regulations. The entry of the old freight station was more concerning than the small area for the parade. The opening LED towards the main entrance across the so called ramp. The ramp was supposed to take all the visitors arriving at the parade. Problem was that the same route including a narrower side ramp west of the main ramp also served as the exit route from the main event V area. It was not the time for Lent Gamba and its owner Riner Scher to organize the parade. They hired a crowd researched to clear the doubts about the safety issues. He made a study about a detailed evacuation in case of danger. Calculation of inflow and outflow if visitors showed that the main ramp was suitable as an entry point, bordered by high walls. It was 85 feet wide and 426 feet long. Its maximum flow would be approximately 115 000 visitors per hour. The most traffic was expected between 1 700 hours and 1 800 hours with almost 1 million of people arriving in the area and 55 000 people leaving. Despite plans and studies, it ended as a disaster. Things complicated even before the event as the festival gates were opened at 11 : 00 am. But due to prolonged contsuctions in central areas, the opening was delayed by 1 hour. When tha gates opened, a large group of people was already waiting and thousands of partygoers lined up from both sides of the tunnel in 1 hour.
The main idea was to drawn the visitors to join the parade and to continue walking along the route. In reality, they obstructed those entering the main area thus slowing down the inflow. The jam at the float's path caused the concentration of people at the main ramp to increase. The entire ramp up to the tunnel was crowded at 14 : 42. Unable to keep the flow of people in and out of the main area, the organizers tried to have support from police. Pushers were engaged those roles was to help people go forward and release the pressure at the main ramp. No one was allowed to leave the site either. What the police believed was a solution only aggravated the situation. The crowd the cordon and the entrance gate didn't reduce. Visitors trying to enter the festival area collided with those wanting to leave. People arriving at the parade was so large that inevitably the cordons would break. The first collapsed at the eastern end followed by the one at the western end. At 16 : 21 a torrent of people rushed towards the main ramp where the third cordon was still holding. As a result no one could move in or out of the area on either side of the police's third cordon. .Some people began climbing poles and traffic signs and other structures to reach the main site above them. Under the crowd's pressure, police dissolved the third cordon, leaving those on the main ramp on their own. Then some of the visitors found a way out via a narrow staircase at the western wall above the tunnel opening.
In a flash, crowd turbulence arose with everyone wanting to climb up. Police tried to control the commotion around them. People kept pouring from the west end of the tunnel making the crowding near the narrow staircases unbearable. When the police removed the fence in the tunnel to let the ambulance pass, hundreds of attendees use the opportunity to rush toward the ramp. Even with the police announcing that the festival area was full and not accessible, it didn't change. Dozens of bodies fell unconscious. Many struggled to stay on their feets. Rainer Schaller, organizer of the parade, meanwhile did an interview describing the parade as a complete success, not aware about the people dying only a couple of yards away. Emergency vehicles began to arrive at the scenes as dozens of people lay on the floor with no sign of life. Police tried to organize and limit the number of people trying to climb the stairs. The density at the ramp reduced but the situation was still critical. Desperate cries for help rang out. Situation cleared up only at 17 : 16 while first fatalities were already reported at 17 : 02.
il y a 8 mois
















